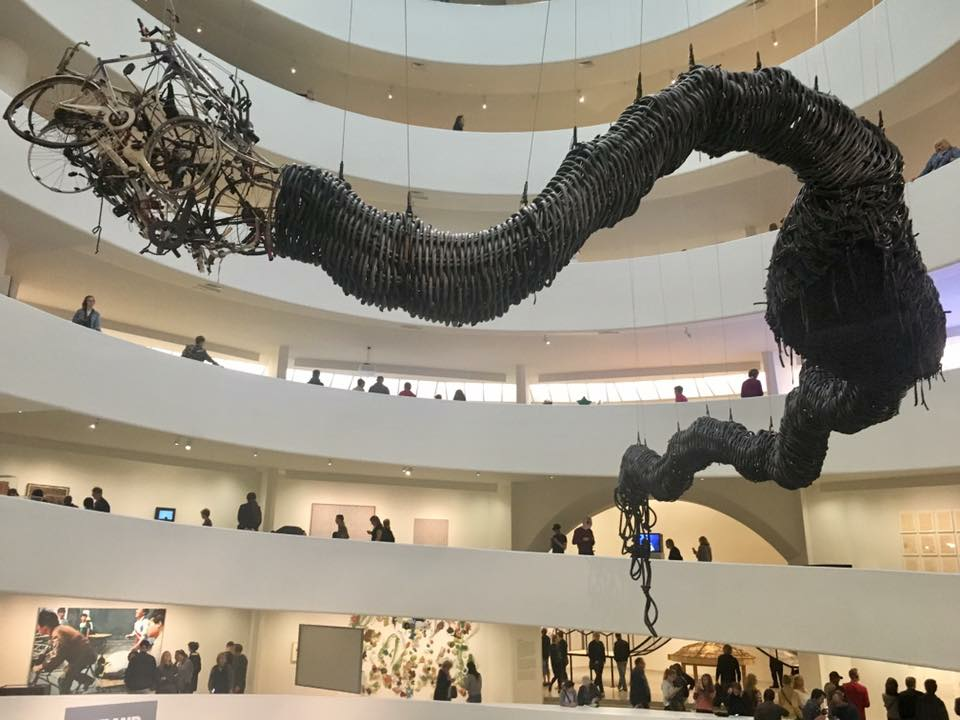
Above is a pic of Chinese artist Chen Zhen’s 1999 sculpture Precipitous Parturition, which currently hangs in the Guggenheim Museum in New York City as part of its Art and China after 1989: Theater of the World exhibit. Zhen “used found materials, weaving black rubber bicycle inner tubes, plastic toy cars, and bicycle parts into a 25-meter-long writhing dragon form. Inspired by a slogan proclaiming: “In 2000, 100 million Chinese people will possess their own cars. Welcome China to participate in the competition of our car industry!,” the work comments on China’s transition from a nation of bicycles into a nation of cars.” If you look at the middle of the sculpture, you’ll see that the dragon is giving birth to an abundance of toy cars, capturing the essence of China’s emerging, globalized economy and culture.
As I listened to the background of Zhen’s art, I immediately thought of a 2001 lecture by the late Peter Drucker:
Let me start out by saying that maybe six weeks ago I had a visit from an old student. Forty years ago, he was a young Taiwanese. In the meantime, he has built a very successful business in Taiwan, and for the last seven years or so has been in Shanghai, where he is now head of a very large joint-venture firm. And I asked him, “What has happened? What’s the most important thing that has happened in China the last three to five years?” And he thought for about five seconds and then said, “That we now consider owning an automobile a necessity and not a luxury.” That is what globalization means. It is not an economic event; it’s a psychological phenomenon. It means that all of the developed West’s values–its mindset and expectations and aspirations–are seen as the norm…It is a fundamental change in expectations and values.[ref]Peter F. Drucker, Rick Wartzman (ed.), “On Globalization” in The Drucker Lectures: Essential Lessons on Management, Society, and Economy (New York: McGraw-Hill, 2010), 215.[/ref]
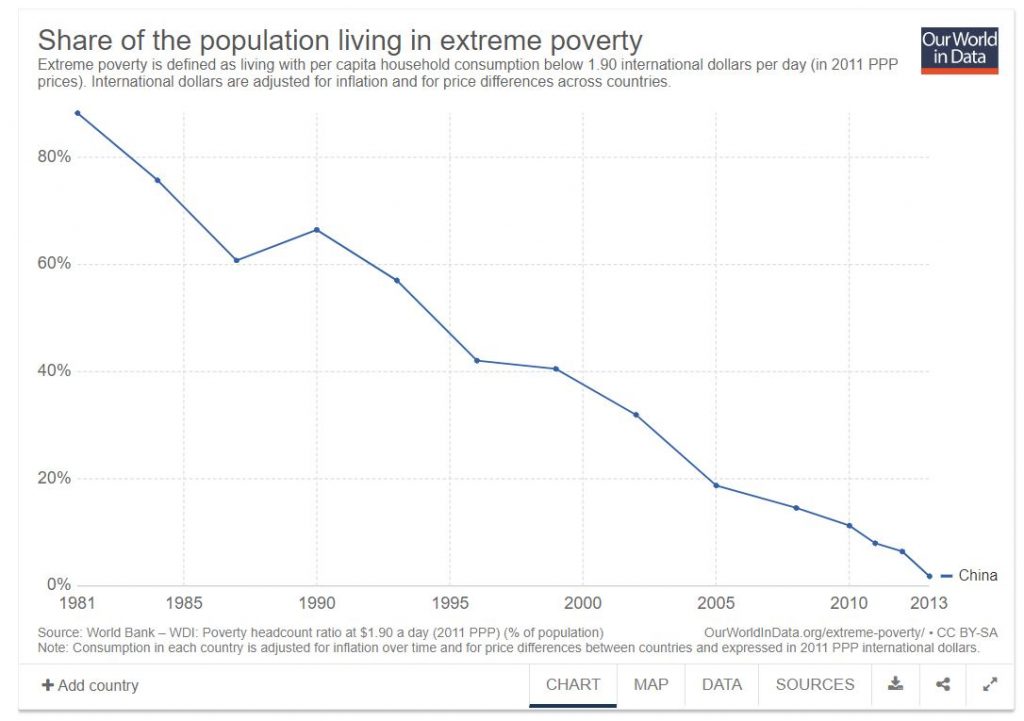
While Zhen may have bemoaned this modern China,[ref]It’s worth noting that even though Zhen grew up in China, he lived in France from 1986 until his death in 2000.[/ref] the country’s heightened participation in the global economy nonetheless yielded enormous benefits for the Chinese people.
Worries over increasing technology, urbanization, and globalization–and the cultural ramifications of it–are too often misplaced. Personally, I find it troubling that people pine over a lost era of poverty and misery. So instead of interpreting the toy cars in Zhen’s piece as a kind of spreading viral infection, perhaps we should see it as a rebirth; as something new and beautiful. Because that’s the only way I can think to describe millions of people being lifted out of extreme poverty.