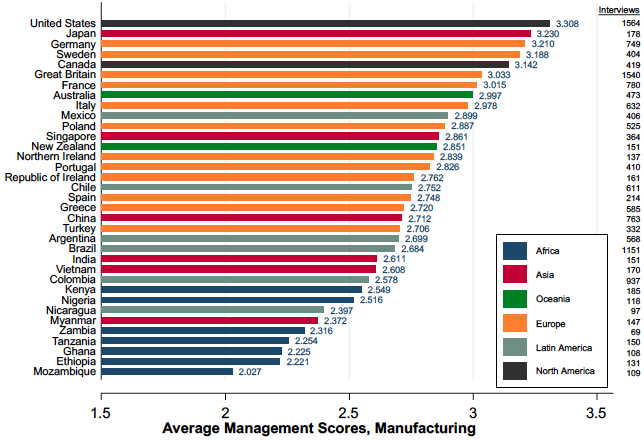
The graph above comes from a recent post by MIT economist John Van Reenen, who has been doing research on the economics of management for the last 15+ years.[ref]Reenen’s work was the foundation of my GBR article.[/ref] He explains,
Many case studies illustrate the importance of management. For example, one I was involved with was Gokaldas Exports (Bloom et al. 2013), a family-owned business founded in 1979 that had grown into India’s largest apparel exporter by 2004. It had 35,000 workers, was valued at approximately $215 million, and exported nearly 90% of its production. Its founder, Jhamandas H Hinduja, had bequeathed control of the company to three sons, each of whom brought in his own son. Nike, a major customer, wanted Gokaldas to introduce lean management practices and put the company in touch with consultants who could help to make this happen. But the CEO was resistant. It took rising competition from Bangladesh, multiple demonstration projects, and finally the intervention of other family members (one of whom I taught in business school) to overcome this resistance. The new practices led to greatly enhanced performance.
Reenen’s work on the World Management Survey has shown that “large, persistent gaps in basic managerial practices…are associated with large, persistent differences in firm performance. Better-managed firms are more productive, grow at a faster pace, and are less likely to die…We performed a simple accounting exercise to evaluate the importance of management for the cross-country differences in productivity. We found that management accounted for about 30% of the unexplained TFP differentials driving the large differences in the wealth of nations.” He concludes,
As our Gokaldas case study mentioned above illustrated, many firms in developing countries may not even realise how weak their management practices are. Or, even when they do they realise this, they may not know how to improve things. Tools such as benchmarking and training can help spread information and knowledge in both of these dimensions. Governments and NGOs often do this, but such programmes are rarely evaluated in a rigorous way (for a survey, see McKenzie and Woodruff 2017). Doing so may be able to raise management and ultimately the wealth of emerging nations.
Once again, management matters.