From The Economist:
Many economists believe that national accounts may underestimate the economic significance of technological innovations. Despite the advent of the internet, smartphones and artificial intelligence, the official value added by the information industry as a share of GDP has scarcely changed since 2000. What might explain this paradox?
Part of the problem is that GDP as a measure only takes into account goods and services that people pay money for. Internet firms like Google and Facebook do not charge consumers for access, which means that national-income statistics will underestimate how much consumers have benefitted from their rise.
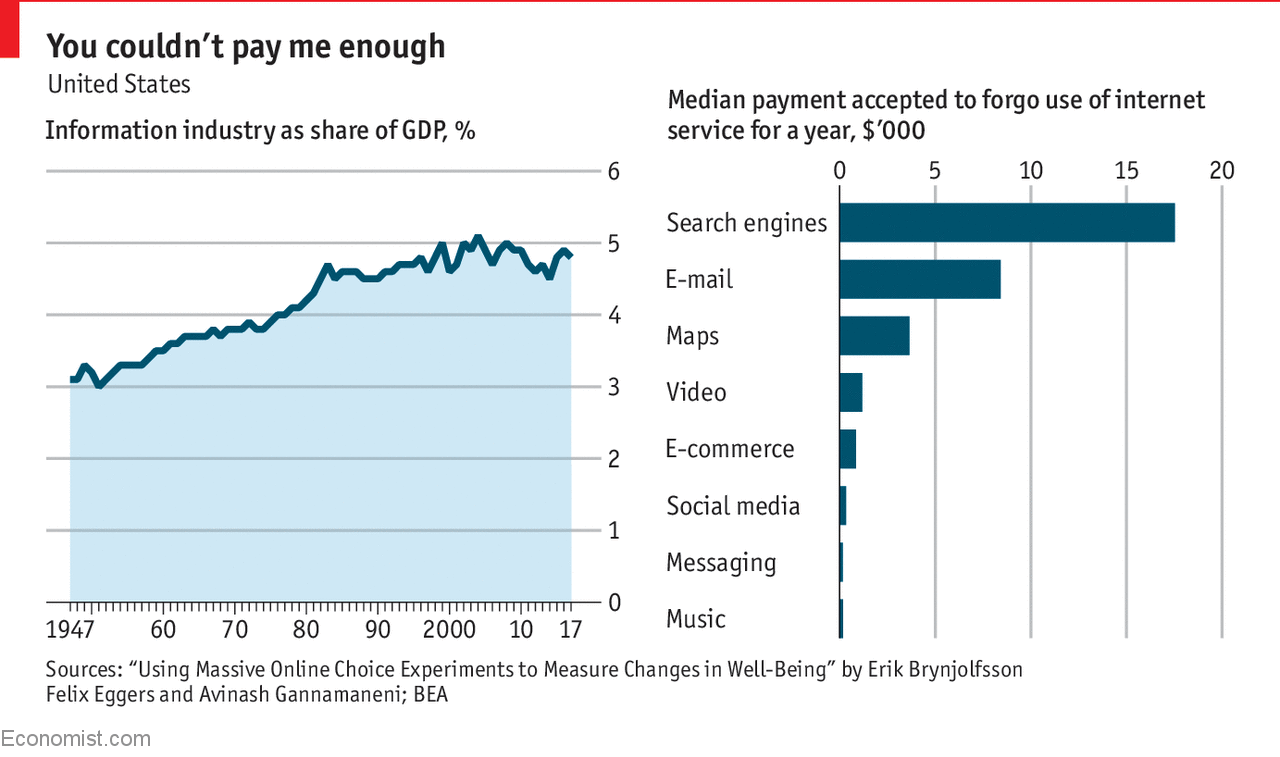
One way to quantify how much these internet services are worth is by asking people how much money they would have to be paid to forgo using them for a year. A new working paper by Erik Brynjolfsson, Felix Eggers and Avinash Gannamaneni, three economists, does exactly this and finds that the value for consumers of some internet services can be substantial. Survey respondents said that they would have to be paid $3,600 to give up internet maps for a year, and $8,400 to give up e-mail. Search engines appear to be especially valuable: consumers surveyed said that they would have to be paid $17,500 to forgo their use for a year.
Recall the thought experiment put forth by The Washington Post: “Try this thought experiment. Adjusted for inflation, would you rather make $50,000 in today’s world or $100,000 in 1980’s? In other words, is an extra $50,000 enough to get you to give up the internet and TV and computer that you have now?”