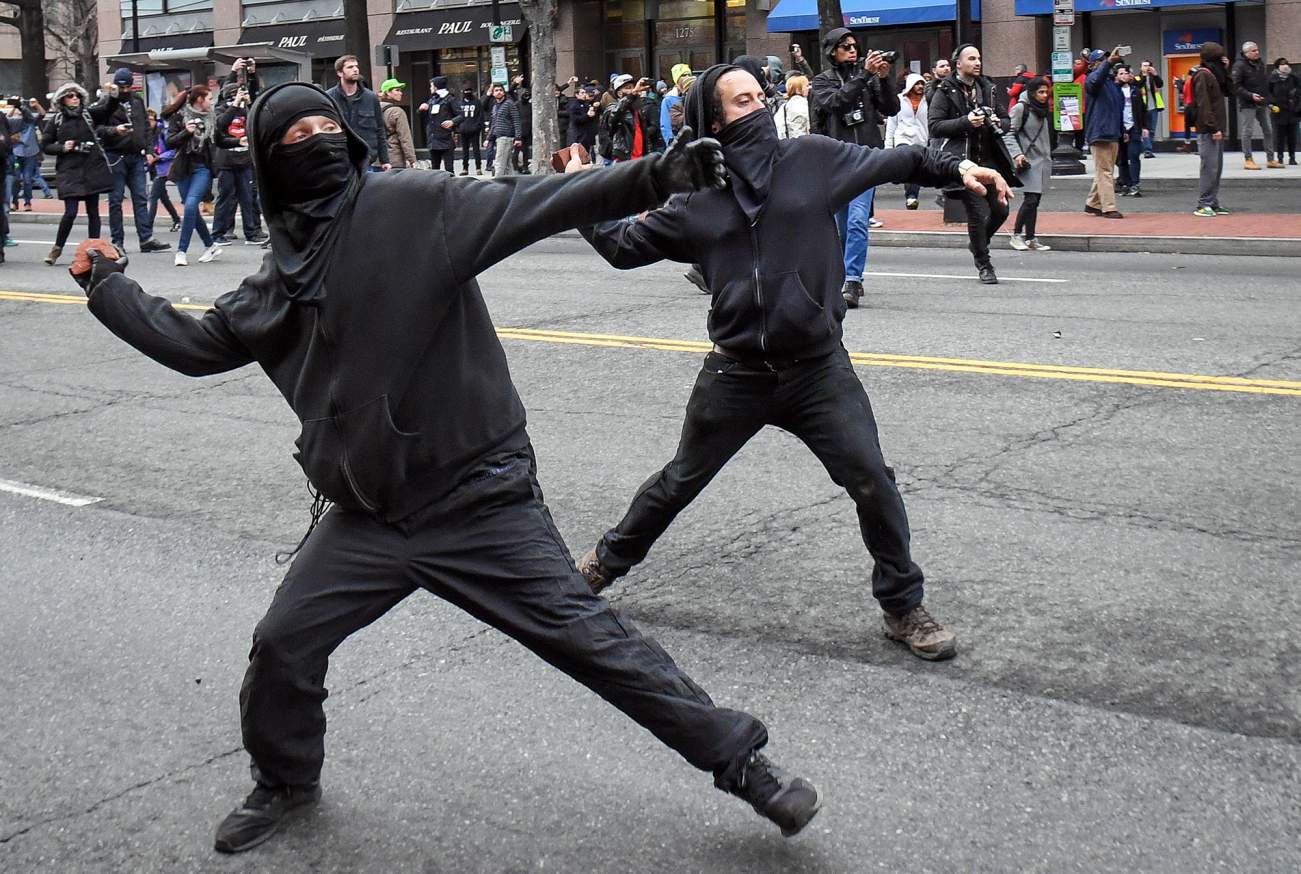
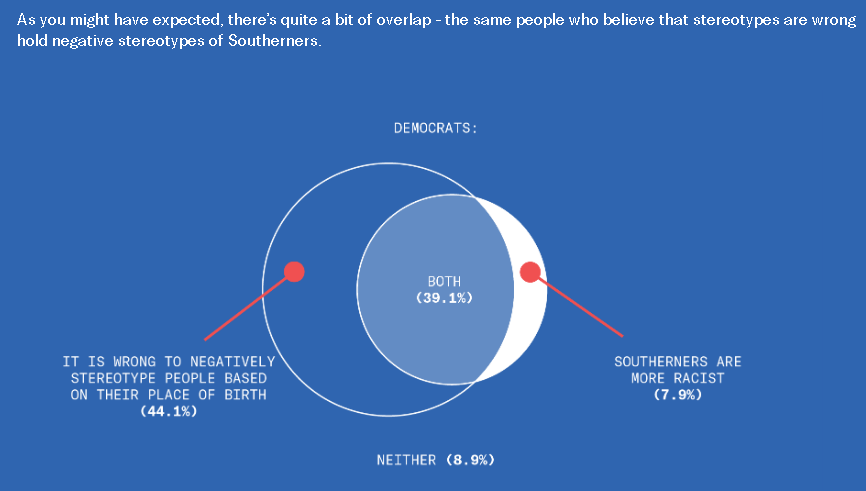
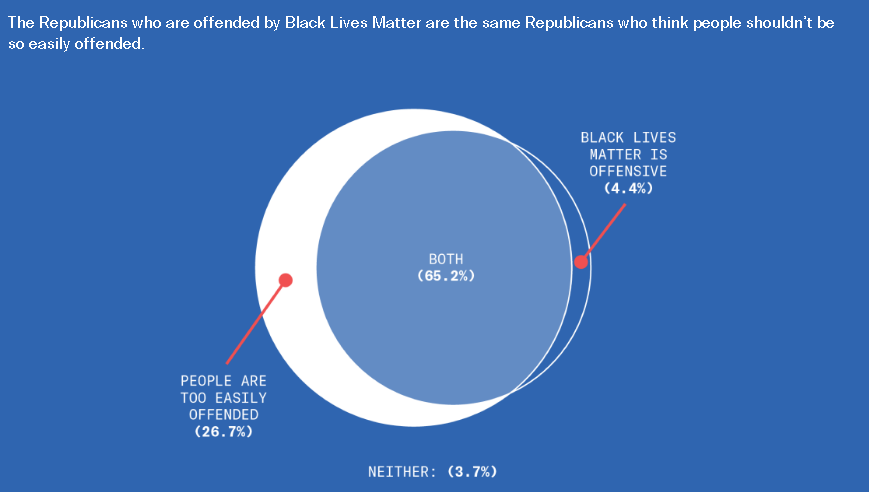
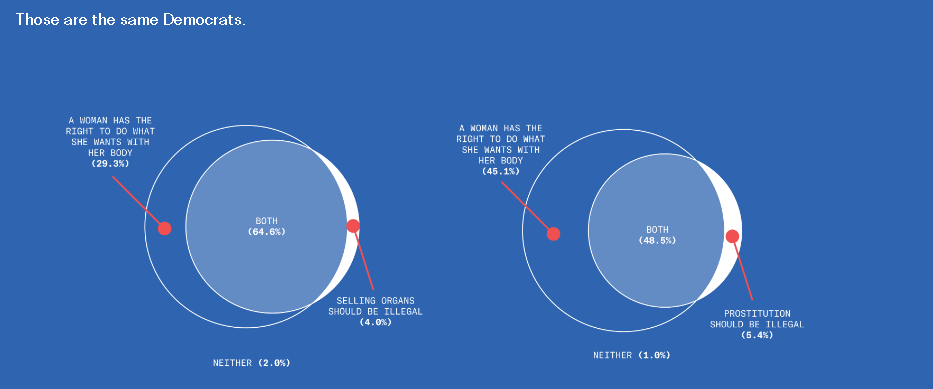
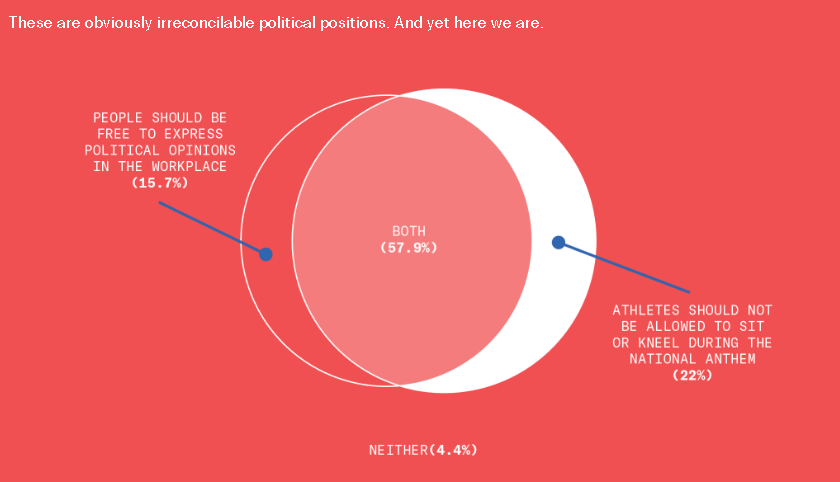
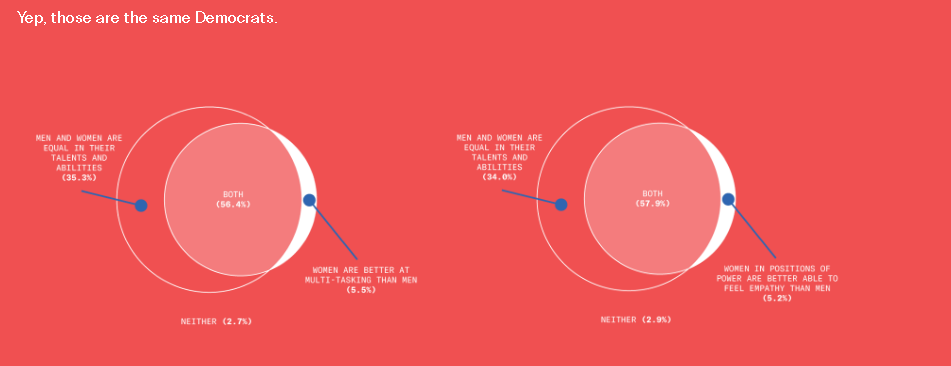
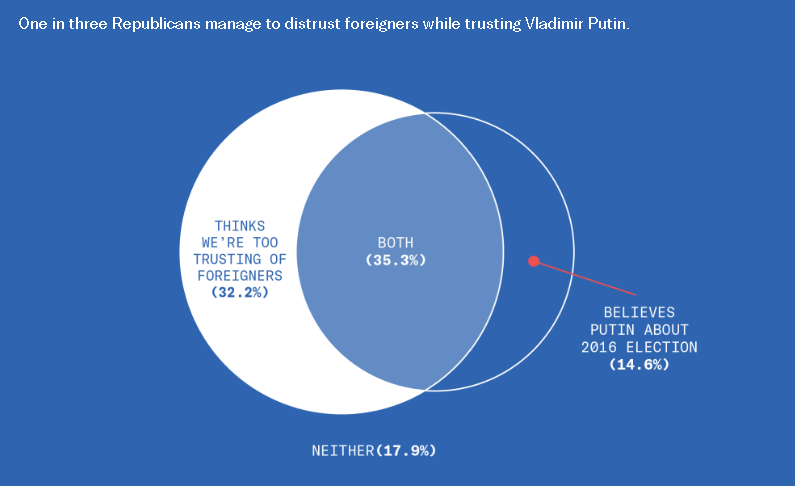
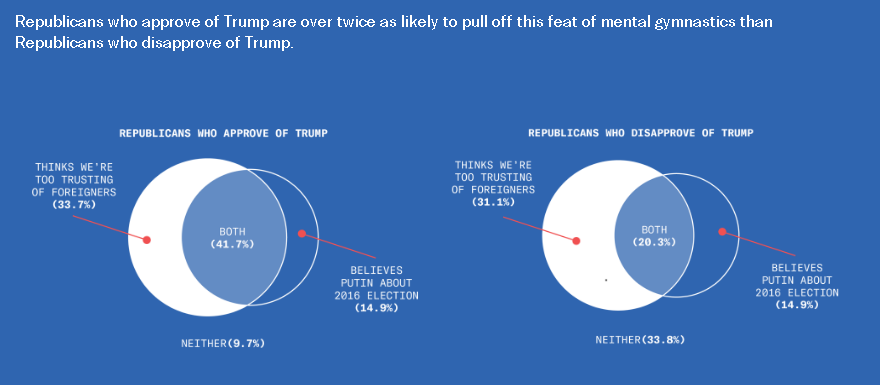
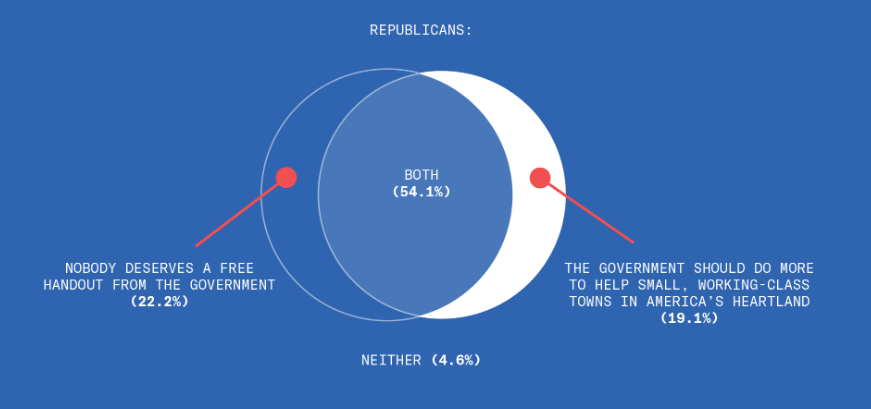
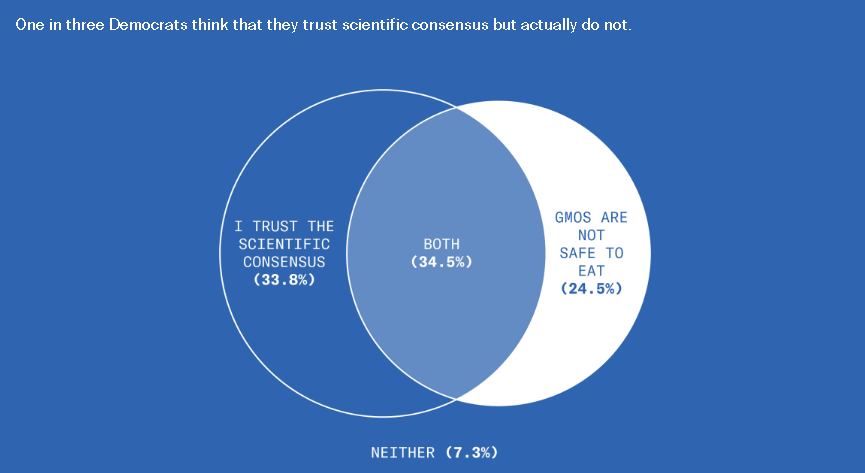
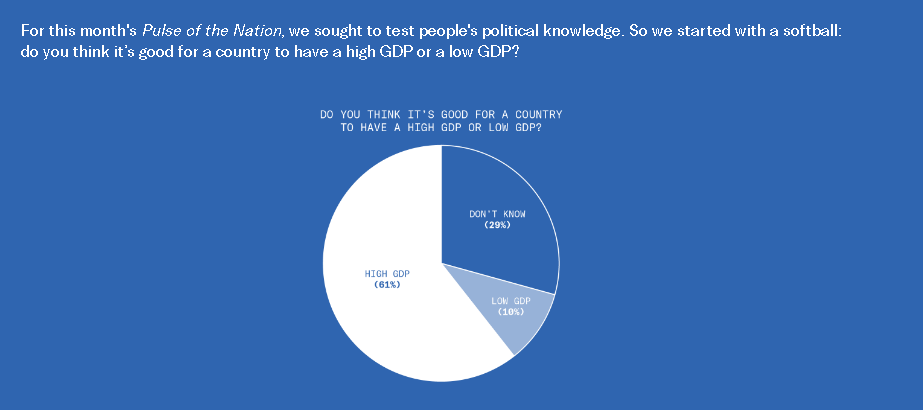
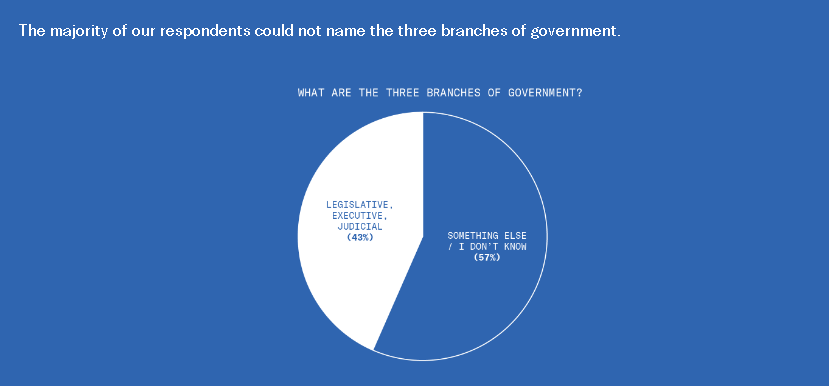
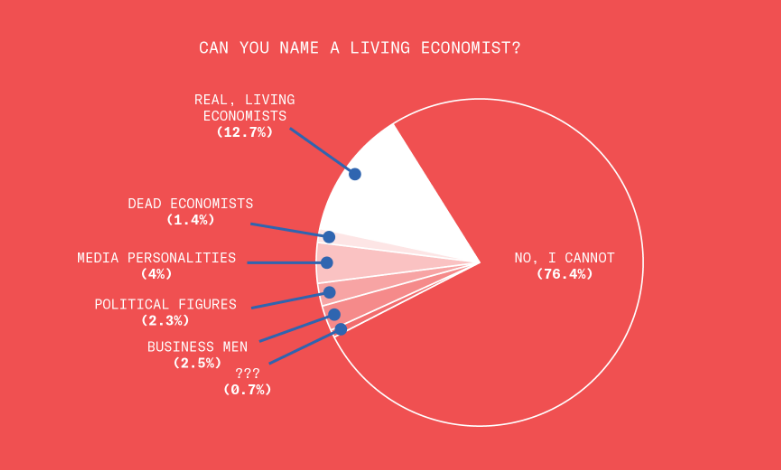
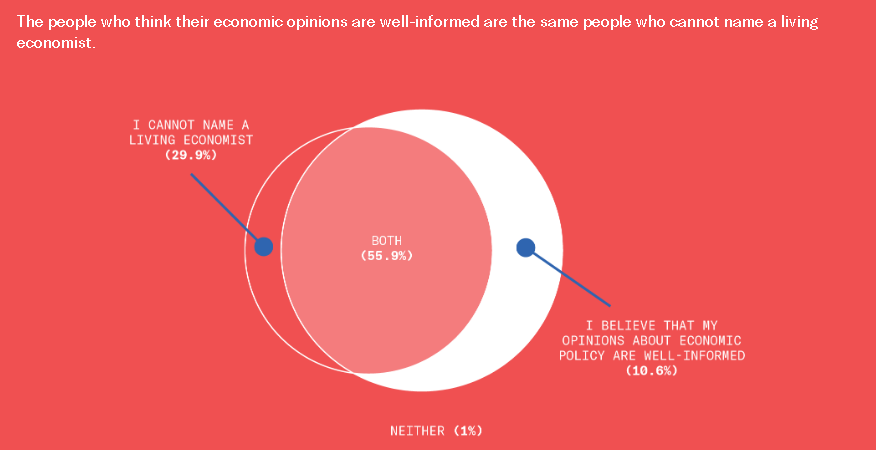
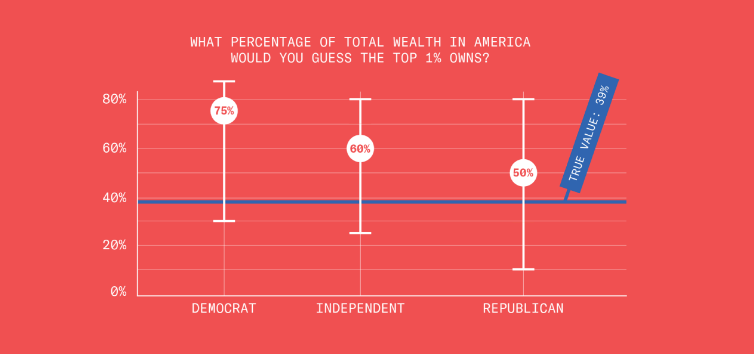
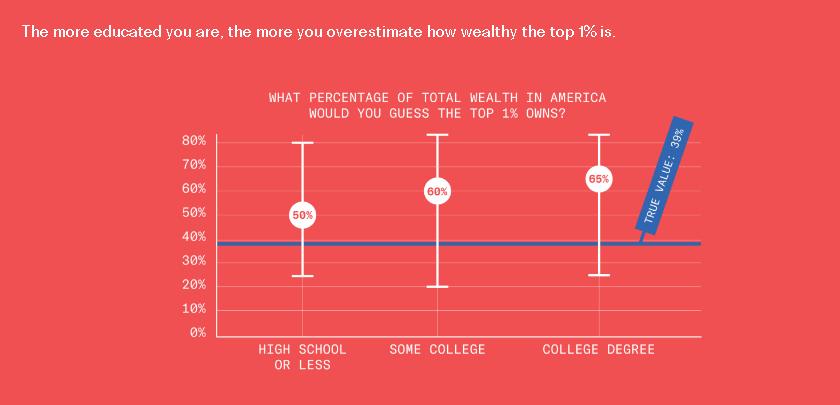
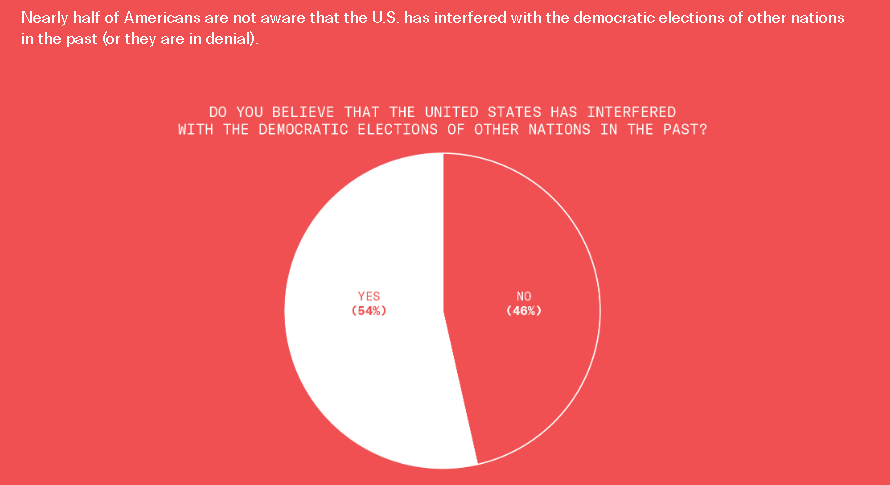
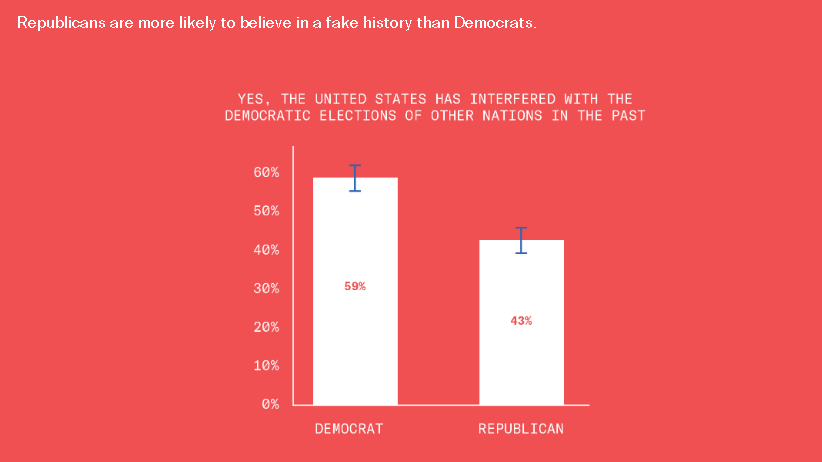
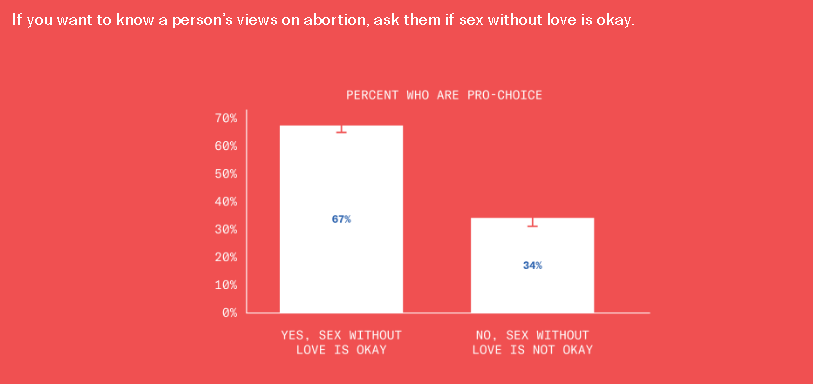
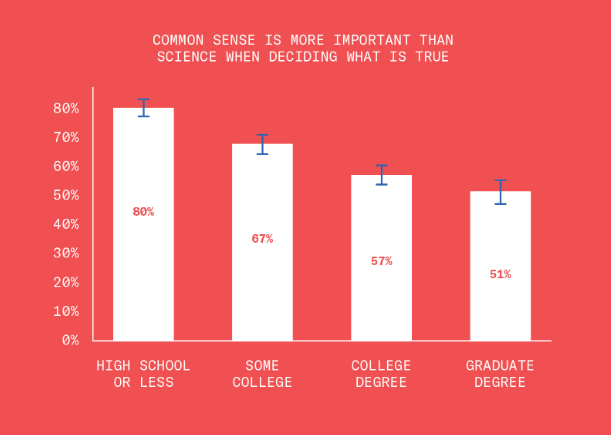
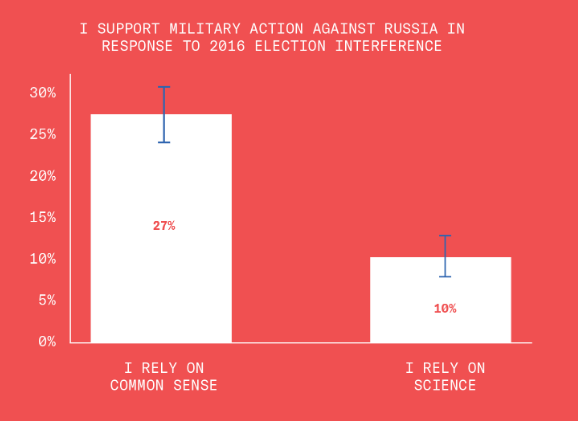
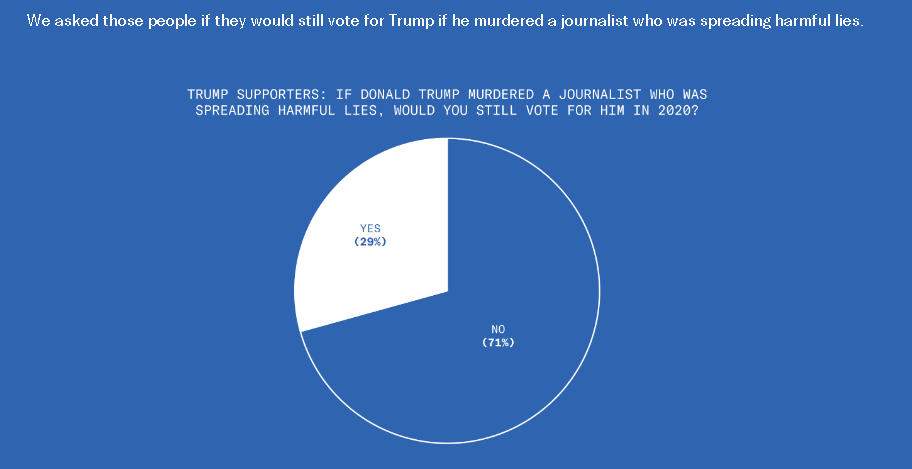
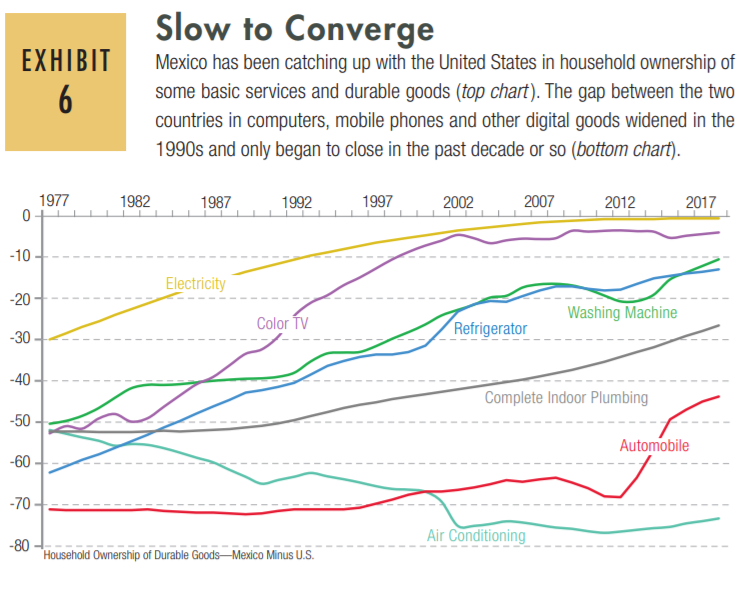
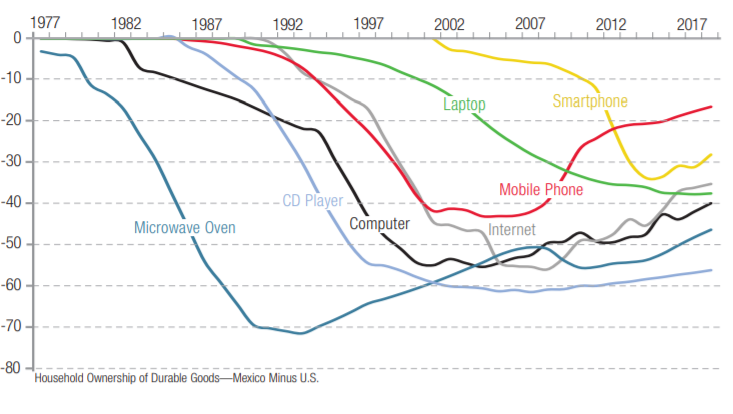
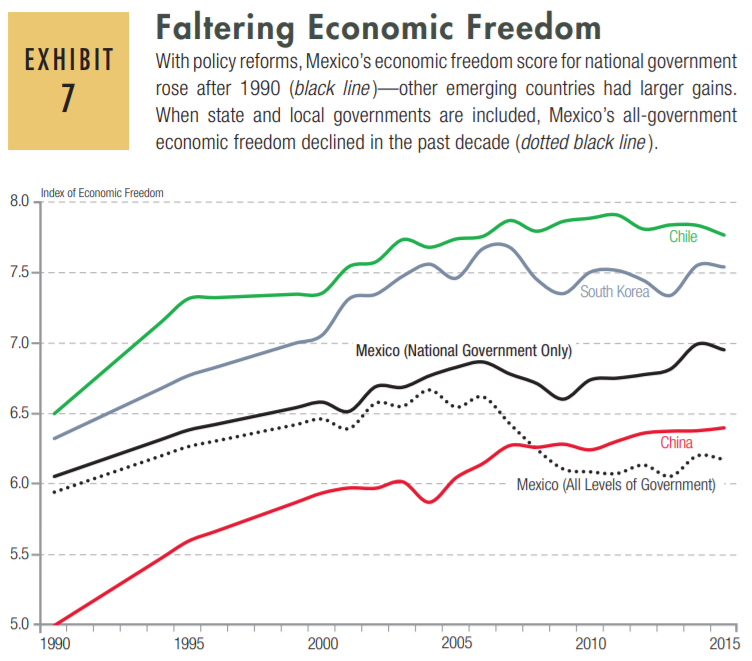
This is disturbing, if not really all that surprising. From the Greater Good Science Center:
Earlier this year, political scientists Lilliana Mason and Nathan Kalmoe presented a paper at the American Political Science Association’s annual meeting, titled “Lethal Mass Partisanship.” With data from two different national surveys, they found that 24 percent of Republicans and 17 percent of Democrats believe that it is occasionally acceptable to send threatening messages to public officials. Fifteen percent of Republicans and 20 percent of Democrats agree that the country would be better if large numbers of opposing partisans in the public today “just died,” which the authors call a “shockingly brutal sentiment.” Nine percent of both Democrats and Republicans agree that violence would be acceptable if their opponents won the 2020 presidential election.
So drives political violence? First and foremost, aggression:
By far the biggest predictor of lethal partisanship across the board was having aggressiveness as a personality trait. This isn’t surprising, of course—aggression and violence go hand in hand. But a deeper look at aggression reveals how it fits together with other traits and shapes human behavior. Aggression all by itself is not good or bad; any of us can become aggressive when we face a direct threat. But aggression can go too far when inner and outer restraints are absent.
In neurological studies, more aggressive people tend to show less activation of the default mode brain network, which is associated with empathy and emotion regulation, which in turn helps suppress aggressive impulses. As psychologist Scott Barry Kaufman notes in Scientific American, aggressive people are more likely to retaliate when treated unfairly by others, which is not necessarily a bad thing (“although they tend to care much less about whether others are treated unfairly”).
However, aggression also shapes political outcomes. “Politicians who are more antagonistic get more media attention and are more often elected than more agreeable politicians,” he writes. “In the general population, antagonistic people are more likely to distrust politics in general, to believe in conspiracy theories, and to support secessionist movements.” In a series of experiments published in 2014, Kalmoe found “that exposure to mildly violent political metaphors such as ‘fighting for our future’ increased general support for political violence among people with aggressive personalities.”
Next, party identity:
After aggressiveness, Mason and Kalmoe found that “partisan identity strength”—how much being Democrat or Republican is part of who they are—is the most important factor in endorsing violence.
There are many studies—mostly from political science and sociology—showing that more Americans are using their political party affiliation as a source of meaning and social identity, with these identities linked to differences in “leisure activities, consumption, aesthetic taste, and personal morality,” as Daniel DellaPosta and colleagues write in their 2015 paper, “Why Do Liberals Drinks Lattes?”
Worse, the Republican Party has become whiter in recent decades, while the Democratic Party has become more racially diverse—which could be intensifying party antagonism. A recent study of survey data by political scientist Diana Mutz found that nothing predicted support for Donald Trump more than a feeling of threatened status among white Christians—an insight ratified by several studies from Robb Willer at Stanford Universityand the Public Religion Research Institute.
…“All of the research to date was pointing in this direction,” adds Mason in an interview. “But we have a long tradition of treating partisanship like a largely benevolent force. It makes sense that as an identity grows stronger, and conflict intensifies, people will begin to approve of violence.”
Third, emotions like anger, contempt, and disgust:
While Mason and Kalmoe’s study gives us some sense of how common the tendency to accept political violence is—and some of the personality traits and belief structures that may be associated with it—a 2015 study points us in the direction of the emotions involved. In “The Role of Intergroup Emotions in Political Violence,” San Francisco State University researchers David Matsumoto and Hyisung C. Hwang and the University at Buffalo’s Mark G. Frank tried to figure out which emotions can drive violence by a group against an outgroup.
They examined the emotional tone of major political speeches that occurred prior to political events throughout history, looking at the emotions expressed in words, the judgments underlying the emotions, and the nonverbal expression of the emotions that could be seen in video form.
They also examined speeches made by “ideologically driven” leaders who despised opponent outgroups that resulted in violence, such as Hitler’s; and they studied those that did not, like Gandhi’s Salt March and pro-Tibet protests at the Beijing Olympics in 2008.
They found that speeches which preceded violent events tended to express more anger, contempt, and disgust (ANCODI)—but not fear, happiness, sadness, or surprise. These negative emotions tended to target specific “outgroups”—Jews, in the case of Hitler’s speeches.
Fourth, moralizing language:
Earlier this year, a team of five researchers searched the popular social media platform Twitter for tweets about the Baltimore protests. They wanted to investigate “moralizing” tweets—that is, tweets that viewed the protests as a moral issue rather than as a political disagreement. A moralizing tweet might, for example, refer to people as “disgusting” or “evil” or “traitorous.”
In fact, they did find a positive association between the number of moral tweets and the occurrence of violent protests (gauged with arrest data). “The days in which there were violent protests, we saw that there was a lot more moral language being used,” says study co-author and University of Southern California Ph.D. student Joe Hoover. “Which was consistent with the idea that morality and violence in these contexts might be linked.”
The team also ran an experiment using another prominent protest marred by violence: the far-right rally in Charlottesville, Virginia, in 2017. Respondents were asked to what extent they thought protesting against the far-right demonstrators was a moral issue; they were then asked how acceptable it was to use violence against these far-right activists. What they found is that people were more likely to embrace violence the more they saw it as a moral issue.
In an additional experiment, the participants were given the same prompts, but they were told either that the majority of Americans agreed with their view of the protest, or that few Americans agreed with their view. They found that “moralization predicted violence only when participants perceived that they shared their moralized attitudes with others.”
In other words, when it comes to violence, there’s validation and safety in numbers. The researchers dubbed this phenomenon “moral convergence,” when many people come together around a strong idea of what’s right and what’s wrong. The “risk of violent protest, in other words, may not be simply a function of moralization, but also the perception that others agree with one’s moral position, which can strongly be influenced by social media dynamics,” they write.
Finally, group leadership:
There are many, many studies—starting with Stanley Milgram’s classic electric-shock experiments—which show that people are much more likely to inflict pain on others when an authority figure tells them to. When leaders engage in violent rhetoric, so do their followers; when they urge calm, people do calm down. Research has documented that words do have an impact on both beliefs and behaviors.
For example, a 2017 Polish study found “frequent and repetitive exposure to hate speech leads to desensitization to this form of verbal violence and subsequently to lower evaluations of the victims and greater distancing, thus increasing outgroup prejudice.” As part of the study, researchers surveyed participants on how frequently they encountered hate speech against refugees; they found that those who were more exposed to hateful words were more prejudiced against the group and more accepting of restrictive immigration policy.
Taken together, these studies suggest that our political leadership—everyone from pundits on cable news to the President of the United States—would do well to avoid promoting the political tribalism that leads people to strongly identify with one group and demonize the other.
In short, watch your aggression, avoid identity politics, keep your emotions in check, lay off the moral grandstanding, and quit putting so much stock into political leaders and pundits.