Update: I wrote a follow-up to this piece: Further Thoughts on World Building

I just finished reading Brandon Sanderson’s monstrous tome: Words of Radiance. It’s his second book in the Stormlight Archives and, like the first, clocks in at over 1,000 pages. The expression on the clerk’s face in Barnes and Nobles when she picked up the book to hand it to me was priceless: “Wow,” she said as she nearly dropped the book, “This is a commitment!”
I’ve never liked high fantasy taken as a genre, but I did love The Lord of the Rings (which launched the genre) and I am enjoying Sanderson’s Stormlight Archives. Despite the fact that I’m enjoying them, however, they display the systematic problems that have plagued the genre ever since (but not including) Tolkien.
High fantasy, if you’re not familiar with the term, refers to the kinds of fantasy books that have maps in them. Not to mention a glossary, pronunciation guide, appendices, and maybe an index, too. This is because high fantasy is defined largely by its setting: an imaginary world with its own history, cultures, religions, languages, and—of course—magic.[ref]Close relatives of high fantasy include medieval fantasy and epic fantasy. The antithesis (within the fantasy genre) is urban fantasy like the Dresden Files because those books are located primarily within a recognizable version of the world.[/ref]

For all practical purposes, Tolkien invented high fantasy. Of course all the pieces came from Saxon and Norse myths and folklore, but what he created when The Lord of the Rings was first published in the 1950’s was something new. The books were very successful from the early years and have gone on to sell more copies than any other novel (150 million thus far) except A Tale of Two Cities.[ref]Tolkien proves he’s still the king[/ref] The corpus of high fantasy has been and continues to this day to be a long line of Tolkien imitators.[ref]This is starting to change with recent blockbusters like George R. R. Martin’s A Song of Ice and Fire and Patrick Rothfuss’s Kingkiller Chronicles
that emphasize created worlds but also depart from high fantasy conventions. Tolkien remains the paramount figure in the genre, however.[/ref]
The problem is that they have all learned the wrong lesson. They understand that setting defines high fantasy, and they understand that Tolkien’s mastery of world-building fueled his artistic and commercial success, but they fundamentally mistake the product (The Lord of the Rings as a narrative text) with the process (Tolkien’s actual beliefs and practices for world-building).
To correct this confusion we must start with the realization that Tolkien’s world-building was inextricable from his religious faith. He was a devout Roman Catholic and what we call world-building he called sub-creation, which is a term with obvious and deliberate religious connotations. As the Tolkien Gateway puts it:
‘Sub-creation’ was also used by J.R.R. Tolkien to refer [to the] process of world-building and creating myths. In this context, a human author is a ‘little maker’ creating his own world as a sub-set within God’s primary creation. Like the beings of Middle-earth, Tolkien saw his works as mere emulation of the true creation performed by God.
As we delve deeper into Tolkien’s theory of sub-creation, it is useful to contrast his view with that of his friend C. S. Lewis, as Professor Downing has done in a paper called “Sub-Creation or Smuggled Theology: Tolkien contra Lewis on Christian Fantasy” at the C. S. Lewis Institute. C. S. Lewis’s Chronicles of Narnia certainly deserves mention as co-founding the subgenre of high fantasy and, for the most part, his reverence for the work of sub-creation paralleled Tolkien’s. But there were important differences, and those differences are very clear in the different tones and styles of the works and also in the supremacy of The Lord of the Rings over Chronicles of Narnia in historical and literary impact.
Downing points out that, for Tolkien, “engaging one’s creativity is an imitation of God and a form of worship.” For Lewis, by contrast, a work of art had to have a higher purpose than the creative impulse itself. In his famous essay “Sometimes Fairy Stories May Say Best What’s to be Said,” Lewis propounded a dualistic account of artistic creation. The Author writes for the sake of writing, but The Man harnesses this impulse towards some external end. As Downing summarizes Lewis: “[A] writer can’t even begin without the Author’s urge to create, but… he shouldn’t begin without the Man’s desire to communicate his deepest sense of himself and his world.”
The Lewis-Tolkien dialogue on sub-creation is a particularly interesting one for a Mormon to enter because of theological differences over the term “creation.” As Downing notes, C. S. Lewis referred back to the orthodox Christian theology of creation ex nihilo in his discussion of artistic creativity. Lewis wrote in a letter to Sister Penelope:
‘Creation’ [as] applied to human authorship seems to me entirely misleading term. We rearrange elements He has provided. There is not a vestige of real creativity de novo in us. Try to imagine a new primary colour, a third sex, a fourth dimension, or even a monster which does not consist of bits and parts of existing animals stuck together. Nothing happens. And that surely is why our works (as you said) never mean to others quite what we intended: because we are recombining elements made by Him and already containing His meanings.
For Downing, this is a point against Tolkien. Tolkien stressed the independence of sub-created worlds but—as Downing and Lewis point out—there is no such thing as independent creation. Humans create by dividing or combining elements that are already available, not by making new elements. From a strictly orthodox Christian theological perspective, this is a fairly serious indictment of Tolkien’s theory of sub-creation because it draws a deep chasm between the kind of creation in which God engages and the kind of sub-creation in which we may participate. How can we be worshipfully imitating our Father when it turns out that the process in which we are engaged is actually a totally distinct process that only happens to share the same label by linguistic happenstance?

As it turns out, however, a rejection of creation ex nihilo is one of the defining aspects of Mormon theology. As many non-Mormon Christian theologians have also observed the Creation (as depicted in Genesis) is almost exclusively a depiction of creation the way that Tolkien and Lewis and all other writers create: by re-arranging pre-existing materials. After “let there be light,” God’s work is all about separation: light from dark, sea from dry land, and so forth. He doesn’t seem to create the earth, moon, stars, sun, or anything else by calling them into being out of the void, but rather by molding unformed materials. For a Mormon like me, at least, sub-creation is more akin to the Creation of God, not less.
In any case, however, what really matters is that Tolkien viewed sub-creation not merely as just another tool in the writer’s tool belt (along with plotting and characterization, say) but rather as a stand-alone activity that had merit in and of itself. This belief is what allowed Tolkien to be such a profligate world builder. He created vastly more material than ever made it into his books. He called this trove of linguistics, geography, history, myth, culture and genealogy the Legendarium, defined by the Tokien Gateway as “the entirety of J.R.R. Tolkien’s works concerning his imagined world of Arda.”
The relationship between The Legendarium and his literary works (like The Hobbit or The Lord of the Rings) an important one in two ways. First, as noted, the Legendarium is far larger. According to Downing, for example, “Quenya, the elvish tongue… had a vocabulary of several hundred words, with consistent declensions and etymologies” by the time he completed The Lord of The Rings, but only a sparse handful of those words appear in the text. The second is that they are, to a large degree, independent. The Legendarium was not completed for the purpose of writing The Lord of the Rings but as an independent exercise undertaken for its own merits. The stories came later, not as an afterthought, but as a distinct labor with their own objectives and process.
Of course in practice the two activities—the world-building and the story-telling—were intertwined. The point is simply that there were two activities, and Tolkien loved them both.
His reckless and extravagant acts of creation are what, to a large extent, made his fiction seems to vibrant and real. Early in The Lord of the Rings, Frodo is nearly killed by a barrow-wight. If you consult Appendix A you will learn that he had been trapped in the cairn of the last prince of Cardolan. Who was that prince? What was Cardolan? I have no idea, but I also have no doubt that Tolkien’s Legendarium contains the answers to both questions. This is just one example of many—to many to count!—where the characters in The Lord of the Rings came across an abandoned place that was steeped in history and drama not directly related to the story.
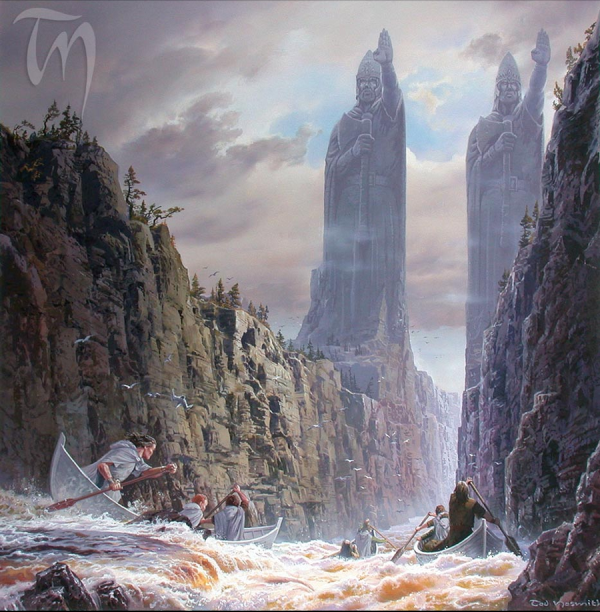

Argonath is, among these many examples, the one that has haunted me for the longest. Here’s the passage, which comes from the chapter “The Great River” near the very end of The Two Towers, that has haunted me since I first read it in a pop-up camper in Tennessee on a summer vacation when I was only 11 or 12 years old:
Upon great pedestals founded in the deep waters stood two great kings of stone: still with blurred eyes and crannied brows they frowned upon the North. The left hand of each was raised palm outwards in gesture of warning; in each right hand there was an axe; upon each head there was a crumbling helm and crown. Great power and majesty they still wore, the silent wardens of a long-vanished kingdom.
What impressed me then and has remained with me ever since is that Arganoth has basically nothing to do with the rest of the story. Sure, it marks the historic northern boundary of Gondor, but by the time we get to The Lord of the Rings, Gondor has already shrunk far from those boundaries. And sure, Strider / Aragorn is a descendent of the antecedents of Gondor, but does that really matter for the story? No, it doesn’t, and that’s why it makes Middle Earth beautiful. It is creation for creation’s sake. I knew, even as a kid, that Tolkien understood perfectly who had built these strange, forgotten pillars and why and the knowledge that he knew things that weren’t in the book is what made the book seem so real. Just like the real world: there’s always more history in Tolkien’s work than you can take in at once. [ref]My confidence was not misplaced, as it turns out. “It was originally constructed about TA 1340 at the order of Rómendacil II to mark the northern border of Gondor,” according to The Lord of the Rings Wiki.[/ref]

So Tolkien loved sub-creation for its own sake, which caused him to do quite a lot of it, which in turn made the setting of The Lord of the Rings vivid beyond compare, which in turn led to the widespread popular love of those books, which in turn helped found the genre of high fantasy. Now, over a half century later, high fantasy is a genre cluttered with books full of maps of fantasy countries and continents, but none of them have remotely captured the grandeur of Tolkien’s original because they have tried to imitate his product without understanding the process that led to it. And Brandon Sanderson’s Words of Radiance (despite being a very fine book) is the perfect example of how it has all gone sideways since Tolkien.
High fantasy writers since Tolkien have created less and showed off more. The bigger problem is not that they have created less in total but rather that the ratio of what they have created for the setting to what they show you on the pages of their novels has diminished substantially. Sanderson’s Stormlight Archives are a great example of this problem because I get the feeling that he very well might, by the time he’s done, eclipse Tolkien in terms of sheer creative output, but he also seems bound and determined to shoehorn every last thought he has ever had about his creations directly into the text. [ref]I’m sure he’s leaving lots out by his own estimation, but compared to Tolkien there’s pretty much nothing left to the imagination at all.[/ref] This has three bad consequences.
First: it makes the stories bloated. Sanderson seems preoccupied with making sure you know exactly how the magical system he has created works. How does that help the story? Did Tolkien need to tell us how Gandalf’s magic worked in excruciating detail? And even if you argue that Sanderson’s strong suit is magical systems where Tolkien’s was language, the metaphor still holds: no one reads The Lord of the Rings and feels like someone tried to sneak a lecture on linguistics into their fantasy novel. The linguistics are there, of course, but Tolkien doesn’t feel the need to beat you over the head with them, whereas large portions of Words of Radiance revolve around nothing other than frog-marching the reader through a tour of Sanderson’s fabricated lore. [ref]Come hell or high water, anyone who finishes the novel will understand the difference between an Honorblade and a Shardblade.[/ref]
Second: it makes the worlds seem flimsy. Far from having an abundance of lost cities and forgotten heroes to populate the fringes of the story, Words of Radiance is rife with extra characters and stories (in the Interludes sections especially) that over-explain the universe. You rapidly get the impression that nothing—no religion, concept, magical power, artifact, civilization, or anything else—is going to be introduced in this book without being explained to death. Reading The Lord of the Rings feels like visiting another world because you know that there is a story underneath every stone, far more than you will actually experience in the text. Reading Words of Radiance feels like visiting a theme park ride by comparison: you have the impression that if you take even one step off the beaten path you’d see the 2×4’s holding up the painted backdrops. No matter how much you create, you have to hold something back or the reader is going to see through your creation.[ref]You can always publish it later in The Silmarillion if you need to.[/ref]
Third: it requires a very specific scope. Because high fantasy authors feel the need to cram every part of their sub-creation into the stories they write and because they often invent their worlds from the very moment of first creation, they trap themselves into writing only cosmic stories. This is bad because Big Questions are easy to raise but hard to answer, and so right off the bat high fantasy writers are painting themselves into a difficult corner. But even if they can pull it off, the fact remains that they are only capable of writing mega-epics. Which, to be clear, is a category that excludes the founding high fantasy story: The Lord of the Rings. Did you notice that the definition of Legendarium included the “world of Arda.” What, exactly, is that? You wouldn’t know, based on reading The Lord of the Rings, just as you would never have heard of Eru Ilúvatar (“the supreme God of Elves and Men” and “the single omnipotent creator”) nor of the Ainur (“divine spirits, the ‘Holy Ones’” who actually shaped Middle Earth).

Tolkien did all the work of sub-creation back to the Big Bang of Middle Earth, and you can read all about it in The Silmarillion, but none of truly foundational lore shows up in The Lord of the Rings at all. It’s true that Sauron is a pretty epic bad guy, but the scope of the The Lord of the Rings is actually quite limited. It’s the story of one particular time that one particular bad guy threatened the peace of one particular region of the world. Gandalf is clear that this isn’t some ultimate final battle or anything like it. He calls the last military campaign “The great battle of our time.” (emphasis added) and when Frodo says “I wish the ring had never come to me. I wish none of this had happened,” Gandalf replies: “So do all who live to see such times. But that is not for them to decide. All we have to decide is what to do with the time that is given to us” (emphasis added). Eru never shows up. Neither do the Ainur. The story of The Lord of the Rings is, compared to the majestic backstory Tolkien had available, mundane. It is almost an anti-epic. It’s emphatically not a story that tries to be about everything all at once and it’s in that specificity that it becomes singular and glorious. I generally dislike high fantasy as a genre precisely because it has lost sight of imperative of specificity that underlies the very definition of narrative.
It’s worth noting at this point an important fact: Tolkien originally tried to include The Silmarillion for publication in the same book as The Lord of the Rings.[ref]According to Wikipedia, but with citations.[/ref] It wasn’t his foresight that saw The Lord of the Rings published as a standalone text, but rather the imposition of editors and publishers who viewed the former work as uninteresting to the public. And they were right: The Silmarillion (which I have read and very much enjoyed) is only good because The Lord of the Rings is great.
The point of this essay is therefore not that Tolkien was an omniscient genius who is the only one to do high fantasy the right way, but simply that his theory of sub-creation is deeply important to the success—both artistically and commercially—of The Lord of the Rings and that anyone who wants to emulate that aspect of his success should study it, understand it, and emulate it.
Tolkien believed in sub-creation as an independently worthy action and engaged in it as a form of worship, and that explains the creation of the vast Legendarium. This was the well from which he dipped to draw out works like The Hobbit and The Lord of the Rings, and it makes sense to think of them as two separate kinds of projects: the world-building vs. the narrative itself.
Subsequent high fantasy authors have failed to fully appreciate this distinction and especially the worthwhile endeavor of sub-creation for its own sake. This is understandable. Writers get in the business to tell stories, not to write thousands of pages of backstory and setting that no one will ever see. They see world-building as necessary to telling fantasy stories, and they see Tolkien praised for the central place his world-building played in The Lord of the Rings, but they end up emulating the final product without fully understanding the process that went into it. They build the world for the story instead of for itself.
What’s more, the process is daunting. It requires an extraordinary amount of work that, in a way, seems wasteful. Why create an entire language—grammar, vocabulary, etymology and all—when just a few fun-sounding syllables here and there will do? The temptation to short-change the world-building and to only build what you need is overwhelming for authors who are not generally flush with cash and are often working on deadlines. How is it possible to justify the kind of exorbitant labor of love that Tolkien has engaged in?
For most people, it isn’t possible, and that is one major reason why The Lord of the Rings still stands alone. No one else seems able or willing to do what Tolkien did. They keep trying to get similar results, however, and I guess that’s good enough for fantasy’s audience.
If all of this sounds a little bit too harsh, let me restate what I said at the outset: even if I hold the genre of high fantasy in low regard as a whole I love The Lord of the Rings and I also like the Stormlight Archives quite a lot. I expect to read all of them.
But I stand by my criticism. It’s not that Sanderson hasn’t invested enough in world-building (he probably has), but it’s more that he just doesn’t seem willing to view that world-building as both intrinsically valuable and distinct from the narrative. He seems to want to cram all of it into the books. And that’s a bad thing. The Stormlight Archives are still excellent, in my opinion, but they are not nearly as good as they could be if they were treated as truly independent stories rather than vehicles for delivering world-building content. An abridged treatment would really, in this case, be a better story. Sanderson could have more focus without Interludes so tangential they make you want to pull your hair out [ref]I read them all, but my brother just started skipping them[/ref], a richer and more immersive world, and greater freedom in the scope he chose to pick. Sanderson is a great writer, but there is still only one J. R. R. Tolkien.