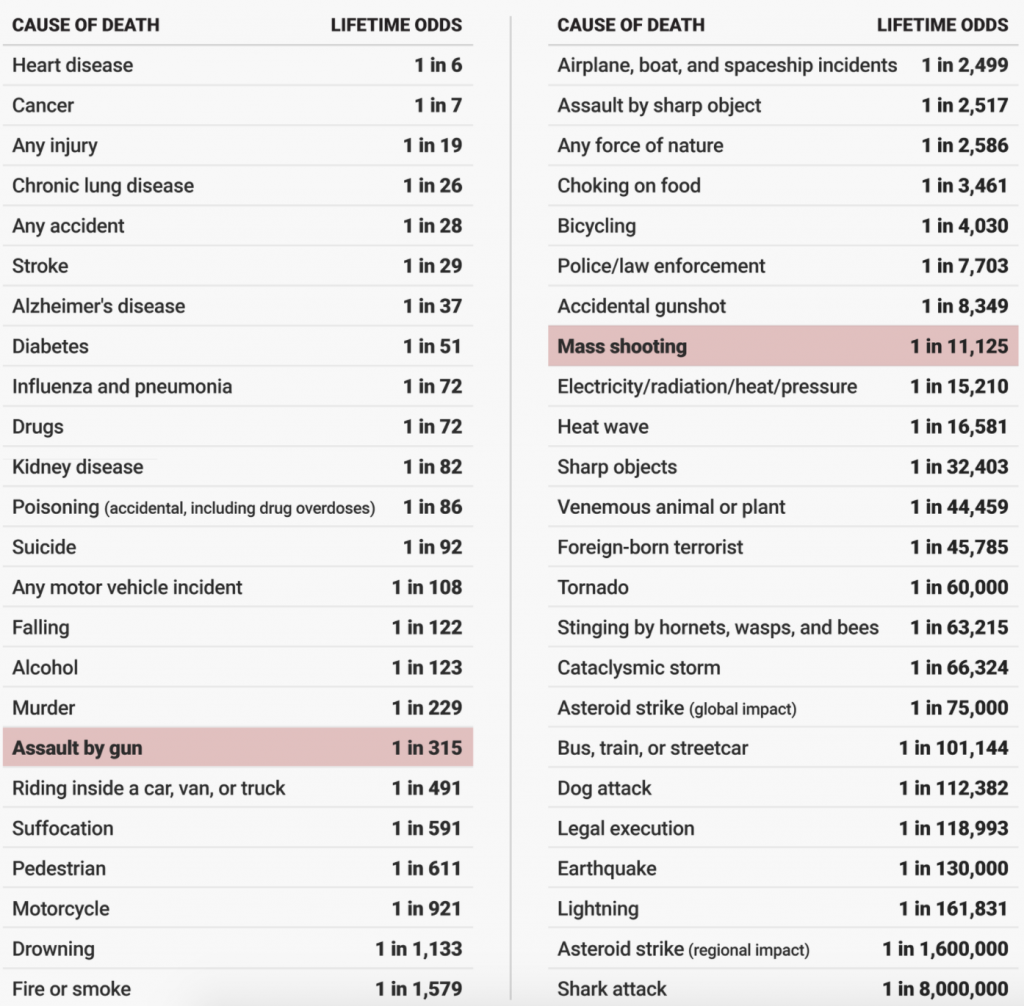
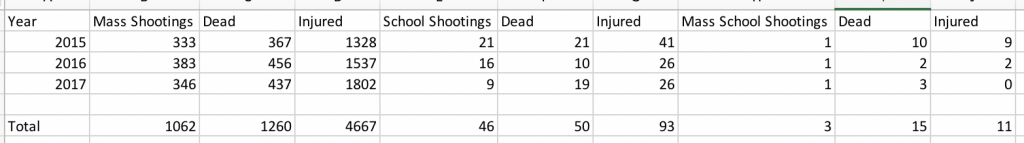
Due to a long-term and acute case of lameness, I never published the DREditors’ best books of 2017. As part of my recover from this lameness-attack, I’m making sure that we get 2019 started off right with a review of the top-5 best books from each of our DREditors. Each who replied, at least. So, here we go!
Ro Givens
The Immortal Life of Henriette Lacks by Rebecca Skloot

Many books like this one have a lot more science in them. This is more of a memoir/biography mixed with some science and medical law. So if you’re looking for a science-focused book, this is not the one, although if you’re looking for a book with no science, this is also not the one. This book tells the story of Henrietta and her family, interwoven with the medical industry’s use of her cervical cancer cells (HeLa), the author’s journey to uncover the family and medical history, and the legal precedents (or lack thereof) involving the consent for and use of human tissue sampled from patients and research subjects. One of the biggest legal takeaways is that if you have tissue separated from you (especially by a medical professional), you likely have no legal claim to it, the medical establishment can do whatever research they want on it, and, in most cases, they can profit from its use.
Hillbilly Elegy: A Memoir of a Family and Culture in Crisis by JD Vance

This book really touches on the cultural aspects of “hillbilly” America that have resulted in poverty throughout much of middle and southern America. It’s not all encompassing, as the author grew up white lower class, and not black, lower class (which brings a host of other issues, but which also has some overlap). Vance often talks about the pervasive feeling that “nothing I do matters” which results in people not trying hard and then blaming everyone else for their problems. He also discusses the feeling that “only other people can be successful”, the inherent tribalism among those who grow up in poverty, and thus the fear of admitting and showing success if you do end up successful. Ultimately Vance believes he “escaped” the poverty cycle because his grandparents didn’t let him hold on to these feelings and provided a safe and stabilizing home – even if he didn’t always live there. But he also benefited from getting into Yale law school – which gives some of the best social capital you can have in America.
Vance’s grandparents were amazing (in both great and crazy ways). I felt a connection to this book having grown up in a broken home (though my mom was the best) with economic difficulties (though not as extreme), with several last names in the household resulting from a complicated family tree, and with my grandfather being the most present father figure in my life. I also connected with the idea of growing up poor and unfamiliar with the academic and business world (my mom never went to college) and then trying to navigate that world all the way through graduate school and beyond. I think the book has the potential to bring empathy, understanding, and laughter to those who have grown up in stable, nuclear families and to bring a feeling of connection to those who have a family skeleton or two in their closets.
When the Air Hits Your Brain: Tales of Neurosurgery by Frank T. Vertosick Jr.

Great read. Not for people who dislike gory details and sad endings, or anyone who needs to avoid webMD-like information for their emotional well-being.
I thought his description of cancer was super interesting.
Cancers and embryos are kindred spirits, both composed of highly mobile cells dividing at full throttle. A fertilized ovum changes from a single cell to a miniature human body in a matter of weeks. During this period of high speed construction, cells migrate freely from one region of the embryo to another, as complex organs are assembled from amorphous cell clusters. The ability of cancerous cells to metastasize to distant sites is a throwback to the migratory properties of embryonic cells. The similarity of cancer cells to embryonic cells goes deeper than a simple capacity to migrate. Proteins and hormones produced in fetal tissues suddenly reappear in cancerous tissues of adults… Mechanistically, cancer results not from the degeneration of adult tissue into decrepit forms, but from their regression into juvenile forms. Cancer cells relive the heyday of their fetal youth… While adult tumors arise from differentiated cells lapsing retrograde into prenatal behavior, pediatric tumors arise from islands of embryonic tissue which never matured in the first place. These “Peter Pan” cells won’t grow up, acting like embryonic tissue even after birth… The fetal nature of these tumors explains why they are so refractory to treatment. Fetal cells have a mission: to create a child. Their drive to complete this mission is so strong that only killing the patient will stop them.
Dr. Frank T. Vertosick, Jr. in “When the Air Hits Your Brain”
Honorable Mention / Fiction
Ready Player One by Ernest Cline aka 1980s Nerd Sci-Fi Explosion

The Martian by Andy Weir aka Space MacGyver

A Discovery of Witches by Deborah Harkness aka An Academic Writes a Vampire Novel

Daughter of the Pirate King by Tricia Levenseller aka Young Female Pirate Captain is the YA Heroine We Need

Walker Wright
In Defense of Openness: Why Global Freedom is the Humane Solution to Global Poverty by Bas van der Vossen and Jason Brennan

With populism on the rise, an empirical and philosophical defense of liberal trade and immigration are both needed. Brennan and van der Vossen give the best case I’ve seen in favor of an open economy, challenging both right-wing and left-wing populists. Perhaps even more important, they defend the notion of productive human rights: the ability to produce, work, build, create, etc. “To leave out productive rights,” they write, “…is not just to distort our picture of human rights and global justice. It’s to distort our picture of people—including the world’s poor. To fully respect people, we must not just make sure that they have enough welfare, happiness, or utility…We must treat them as active and productive agents, as contributors to their own lives and those around them, and no just as consumers or receptacles of goods” (pg. 111).
The Elephant in the Brain: Hidden Motivations in Everyday Life by Kevin Simler and Robin Hanson

In the era of social media, I have become extremely skeptical of people’s public moral grandstanding. Through a wide-ranging empirical investigation, Simler and Hanson demonstrate that I’m right to be skeptical: many of our motives are in fact selfish in nature (color me shocked…). We often seek to gain power and status through the accumulation of social and moral capital. And we do this through various mediums: consumption, charity, politics, religion, and so on. Of course, we are a mixed bag of motivations. But sweeping the selfish ones under the rug for fear of being called cynical does no one any good.
Sex & World Peace by Valerie M. Hudson, Bonnie Ballif-Spanvill, Mary Caprioli, and Chad F. Emmett

The impressive datasets and empirical research found in this book demonstrate the interdependence of macro and microlevel institutions. The authors find that the physical security of women and various factors of gender inequality (e.g., polygyny, inequitable family law) are strongly associated with state-level peacefulness. In sum, gender inequality in customs and law perpetuates state insecurity and war. This is likely why Hudson elsewhere has described companionate heterosexual monogamous marriage as human peace incarnate.
The Power of Godliness: Mormon Liturgy and Cosmology by Jonathan A. Stapley

Priesthood has been a hot button issue in contemporary Latter-day Saint discourse, largely due to debates over gender and ecclesiastical authority. In Stapley’s historical construction, priesthood in the early Church was cosmologically identified with the eternal kinship bonds created and concretized through temple rituals. The eclipse of this understanding and its conflation with ecclesiastical priesthood offices had major effects on future interpretations of both scriptures and ordinances. Stapley’s recovery of this earlier meaning enriches our already temple-oriented theology.
Death (The Art of Living) by Todd May

May is a philosophical advisor for the show The Good Place and it was there that I saw this book briefly mentioned. May argues that death is the most defining feature of human beings since it permeates throughout everything we think, feel, and do. What’s more, he argues that immortality in some ways would undermine meaning by eliminating the sacrifice and urgency associated with time scarcity. As a Latter-day Saint, my theology views mortality as a necessary step in eternal progression toward divinity. Despite the author coming from an atheistic angle, this book offers possible answers as to what role death plays in this training ground for godhood.
Honorable Mention
- The Inclusive Economy: How to Bring Wealth to America’s Poor by Michael D. Tanner
- Global Inequality: A New Approach for the Age of Globalization by Branko Milanovic
- The Great Divorce by C. S. Lewis
- Textual Studies of the Doctrine and Covenants: The Plural Marriage Revelation by William V. Smith
- Enlightenment Now: The Case for Reason, Science, Humanism, and Progress by Steven Pinker
Nathaniel Givens
Unashamed by Lecrae Moore

It’s like I said in my Goodreads review: if I could give this book 6 stars, I would. I started listening to Lecrae after hearing “Just Like You” on a campus bus in Michigan. I memorized enough of the lyrics to look it up when I got home, and from then on I was hooked. Lecrae is one of my heroes with folks like Dustin Kensrue and Josh Garrels: artists who refuse to pick and choose between their faith and their art. Between the world and the kingdom.
This book is Lecrae’s autobiography. It’s an awesom story. It’s well-written. A lot of Lecrae’s excellent lyricism translates from verse to prose just fine. And it’s also full of really insightful Christian theology. I’m pretty sure Lecrae is reformed Calvinist which is pretty different from my ow faith, but it’s OK. It’s OK with me, anyway. What we have in common is much more than what separates us, and I learned–and continue to learn–a lot from Lecrae.
The Apostle Paul wrote, “We are his workmanship, created in Christ Jesus for good works which God prepared beforehand that we should walk in them.” The word for “workmanship” is “poema”. We are God’s poem to the world. A poem articulates the heart, the mind, and the character of the poet. Your calling may not be to write music or produce music or sing music but that’s OK. You are music. You’re God’s music. And God doesn’t just want to break records and top charts with you. He wants to change lives and industries and society. By God’s grace, I’m going to keep making the music as long as I have air in my lungs. But my prayer is that you’ll make music too. Maybe not with your voice. Maybe not on a stage. But hopefully with your life. And may God get the glory from the music we create.
Lecrae in “Unashamed”
Keep on creating.
Destiny Disrupted by Tamim Ansary

I grew up with friends who were Muslim. I learned about Islam in school. I studied Islam a little bit more on my own. But reading Destiny Disrupted was the first time I felt like I really started to get it. The most important insight for me was understanding the extent to which Islam is–and always was–a communal project. I also really enjoyed learning about the stories of the lives of the early successors of Mohammad. Hearing those stories made me think that to understand where someone comes from, you really have to know the stories that they heard as kids. Finally, it’s a tragic story of how the forces of fundamentalism won out over other branches of Islam and sidelined their progress. I can’t recommend this book enough for anyone who is interested in Islam or just wants to read great history.
The moment Mohammed died, the community faced an overwhelming problem. It wasn’t just “Who is our next leader?” but “What is our next leader?” When a saint dies, people can’t simply name some other saint in his placed, because such figures aren’t created by election or appointment, they just emerge; and if they don’t, oh well; people may be disappointed but life goes on. When a king dies, by contrast, no one says, “Wouldn’t it be nice of someday we had another king?” The gap must be plugged at once.
When Prophet Mohammed died, it was like a saint dying but it was also like a king dying. He was irreplaceable, yet someone had to take his place. Without a leader, the Umma could not hold together.
Tamim Ansary in “Destiny Disrupted”
When the Air Hits Your Brain by Frank T. Vertosick, Jr.

I know that Ro already picked this one for her list, but I have to add it to mine, too. I’ve read several medical or scientific autobiographies, but this one is probably the most touching that I’ve ever encountered. It is a book defined by one term that you don’t ordinarily associate with the medical profession, and especially not with neurosurgeons: humility. This book will touch you, and it will also enlighten you. Read it.
You have to care about the patients, but not too much. It’s unethical to operate on our wives. Why? Because we’d be too likely to choke. To get nervous and f–k up if its our own family on the chopping block. The very fact that medical ethics forbids treating your immediate family is proof that we shouldn’t get so involved with a patient that we are made nervous by the possibility of failure. Patients want us to care about them, but they want us to perform with the nerveless demeanor of someone slicing baloney in a deli at the same time. It’s one of those unexplained paradoxes we just accept.
Doctor Frank T. Vertosick, Jr. in “When the Air Hits Your Brain”
The Destroyermen Series by Taylor Anderson

I have had so much fun with this series this year! There are thirteen books in the series, and I read every single one of them. (OK, I listened to them.) The premise is pretty simple. The USS Walker, a World War I-era destroyer that was sent to the Pacific after Pearl Harbor (Walker was a real-life ship) is caught up in a mysterious storm that transports it to an alternate-history version of the Earth where humans never evolved, but other intelligent life forms did. And those other species? They’re at war. Also: dinosaurs. It’s so, so good, and it has grown so, so far from that initial premise. There’s no way that I can summarize 13 books, so just trust me: they’re great.
“Wherever we go, whatever we do in this goofed-up world, somebody or something always needs killing.”
– Jim Ellis, in Taylor Anderson’s novel “Firestorm”
A World Undone: The Story of the Great War, 1914 – 1918 by G. J. Meyer

This is the best history of World War I I’ve read since Guns of August, and I’d even say it’s better than Guns of August. It’s always amazing to me how badly wrong everything I learned about history in high school was, and this is no exception. A lot of that is on me. What can you really teach a sheltered teenager about the Great War? Not much. So, yeah, a lot of what I learned about trench warfare was wrong. The combat in World War I was much more dynamic, even on the Western Front, than what I was taught. But the utter, monumental, tragic senselessness of it all? I was told about it, but it didn’t sink in. Of course I don’t believe I cna understand it now like someone who lived through it then, but at least a glimmer of it finally got through to me while reading this sweeping, majestic, terrible history.
“Among this chaos of twisted iron and splintered timber and shapeless earth are the fleshless, blackened bones of simple men who poured out their red, sweet wine of youth unknowing, for nothing more tangible than Honour or their Country’s Glory or another’s Lust of Power. Let him who thinks that war is a glorious golden thing, who loves to roll forth stirring words of exhortation, invoking Honour and Praise and Valour and Love of Country. Let him look at a little pile of sodden grey rags that cover half a skull and a shin bone and what might have been its ribs, or at this skeleton lying on its side, resting half-crouching as it fell, supported on one arm, perfect but that it is headless, and with the tattered clothing still draped around it; and let him realise how grand and glorious a thing it is to have distilled all Youth and Joy and Life into a foetid heap of hideous putrescence.”
Excerpt from a letter by Roland Leighton to Vera Brittain in August 1915 as quoted by G. J. Meyer in “A World Undone”
Honorable Mention
- The Collected Stories of Arthur C. Clarke by Arthur C. Clarke – In which I learned from a grand master of sci-if.
- Kings of the Wyld by Nicholas Eames – Equal parts epic fantasy and rock-and-roll.
- Off to be the Wizard by Scott Meyer – What happens when you discover the file that lets you edit reality. I.e. hijinks ensue.
- Deadly Assessments by Drew Hayes – Our favorite undead accountant is back in a fresh installment that doesn’t feel undead at all.