
I’ve mentioned in passing the oddity of Democrats being more supportive of free trade than their supposedly capitalism-loving Republican opponents. A brand new poll by POLITICO and the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health further confirms this shift. Some of the findings:
- 47% of Republicans think free trade has hurt their communities, twice that of Democrats (24%). Only 18% of Republicans think free trade has helped, while nearly twice as many Democrats do (33%).
- When broken down by country (Canada, EU, Japan, South Korea, Mexico, China) and by party, Republicans exceed both Democrats and Independents on every country in claiming that trade hurts. Over 60% of Republicans think trade with Mexico and China have hurt Americans. Democrats were surprisingly the lowest on every country.
- “54% of Democrats believe that free trade has lost more U.S. jobs than it has created, compared to 66% of Independents and 85% of Republicans. Similarly, 38% of Democrats believe free trade has lowered U.S. wages, compared to 50% of Independents and 66% of Republicans. Only 8% of Republicans, 11% of Independents, and 19% of Democrats think free trade has led to higher wages for U.S. workers” (pg. 3).
There’s much more, including attitudes about the state of the economy and the Affordable Care Act. As one who grew up in a conservative household, I find this all rather worrying. As Trump’s senior policy adviser and economist Peter Navarro told POLITICO, “There’s been a schism for a long time between registered Republicans and the party leadership. That was the essence of the primary election. You had a group of insider politicians singing the same old globalization song. And one candidate saying the emperor has no clothes.” The problem, of course, is that the emperor is fully–clothed.
The Republican party has become a party of mercantilists.


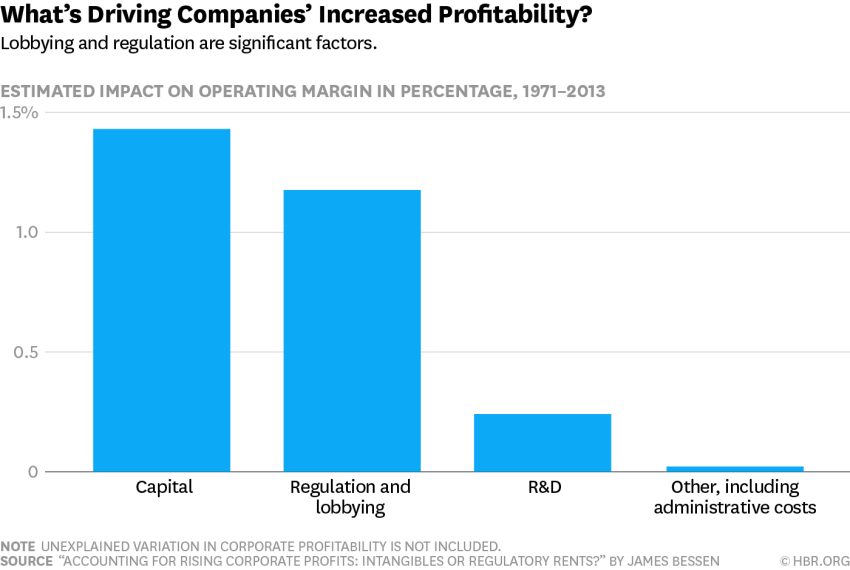
 …Imagine that this whole system is going on at the same time that IKEA spends millions of dollars lobbying senators about chair-related issues, and that these same senators vote down a bill preventing IKEA from paying off other companies to stay out of the chair industry. Also, suppose that a bunch of people are dying each year of exhaustion from having to stand up all the time because chairs are too expensive unless you’ve got really good furniture insurance, which is totally a thing and which everybody is legally required to have.
…Imagine that this whole system is going on at the same time that IKEA spends millions of dollars lobbying senators about chair-related issues, and that these same senators vote down a bill preventing IKEA from paying off other companies to stay out of the chair industry. Also, suppose that a bunch of people are dying each year of exhaustion from having to stand up all the time because chairs are too expensive unless you’ve got really good furniture insurance, which is totally a thing and which everybody is legally required to have.




 Martin Shkreli, hedge fund manager and founder of Turing Pharmaceuticals, has been
Martin Shkreli, hedge fund manager and founder of Turing Pharmaceuticals, has been 