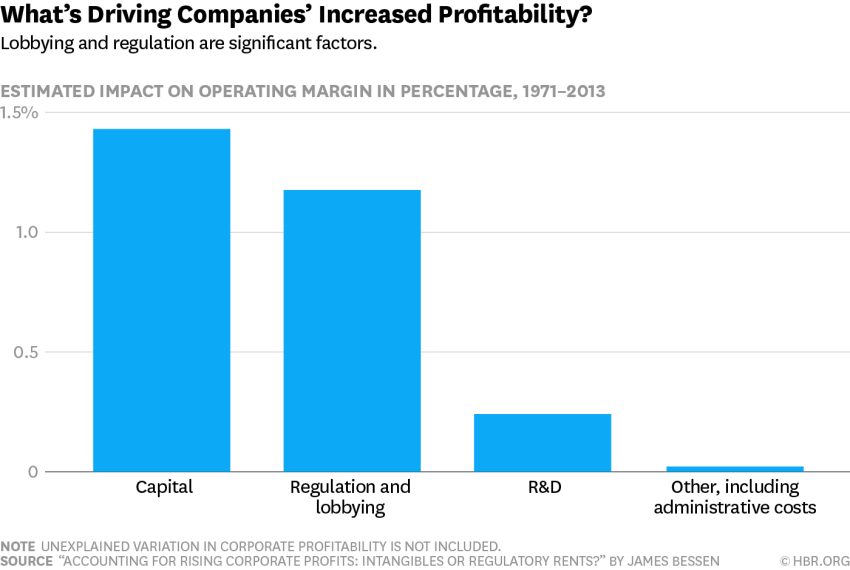
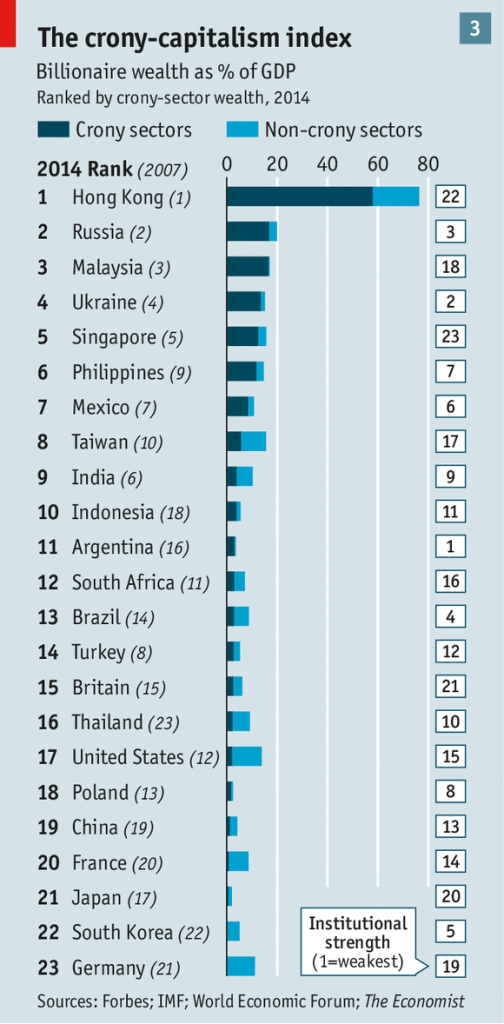
There is another pharma scandal in the news over the astronomical increase in EpiPen’s price. Yet, before we begin to blame and denounce the abstraction “capitalism” for all our woes, it might be useful to recall my post on the Shkreli/Daraprim scandal and its discussion of healthcare regulations. This new case appears to be incredibly similar and the site Slate Star Codex has an excellent post contrasting the way the drug industry operates compared to the chair industry:
when was the last time that America’s chair industry hiked the price of chairs 400% and suddenly nobody in the country could afford to sit down? When was the last time that the mug industry decided to charge $300 per cup, and everyone had to drink coffee straight from the pot or face bankruptcy? When was the last time greedy shoe executives forced most Americans to go barefoot? And why do you think that is?
The answer?:
The problem with the pharmaceutical industry isn’t that they’re unregulated just like chairs and mugs. The problem with the pharmaceutical industry is that they’re part of a highly-regulated cronyist system that works completely differently from chairs and mugs.
If a chair company decided to charge $300 for their chairs, somebody else would set up a woodshop, sell their chairs for $250, and make a killing – and so on until chairs cost normal-chair-prices again.
And in his final act, he drives the point all the way home (worth quoting at length):
Imagine that the government creates the Furniture and Desk Association, an agency which declares that only IKEA is allowed to sell chairs. IKEA responds by charging $300 per chair. Other companies try to sell stools or sofas, but get bogged down for years in litigation over whether these technically count as “chairs”. When a few of them win their court cases, the FDA shoots them down anyway for vague reasons it refuses to share, or because they haven’t done studies showing that their chairs will not break, or because the studies that showed their chairs will not break didn’t include a high enough number of morbidly obese people so we can’t be sure they won’t break. Finally, Target spends tens of millions of dollars on lawyers and gets the okay to compete with IKEA, but people can only get Target chairs if they have a note signed by a professional interior designer saying that their room needs a “comfort-producing seating implement” and which absolutely definitely does not mention “chairs” anywhere, because otherwise a child who was used to sitting on IKEA chairs might sit down on a Target chair the wrong way, get confused, fall off, and break her head.
…Imagine that this whole system is going on at the same time that IKEA spends millions of dollars lobbying senators about chair-related issues, and that these same senators vote down a bill preventing IKEA from paying off other companies to stay out of the chair industry. Also, suppose that a bunch of people are dying each year of exhaustion from having to stand up all the time because chairs are too expensive unless you’ve got really good furniture insurance, which is totally a thing and which everybody is legally required to have.
And now imagine that a news site responds with an article saying the government doesn’t regulate chairs enough.