1.Good Intentions
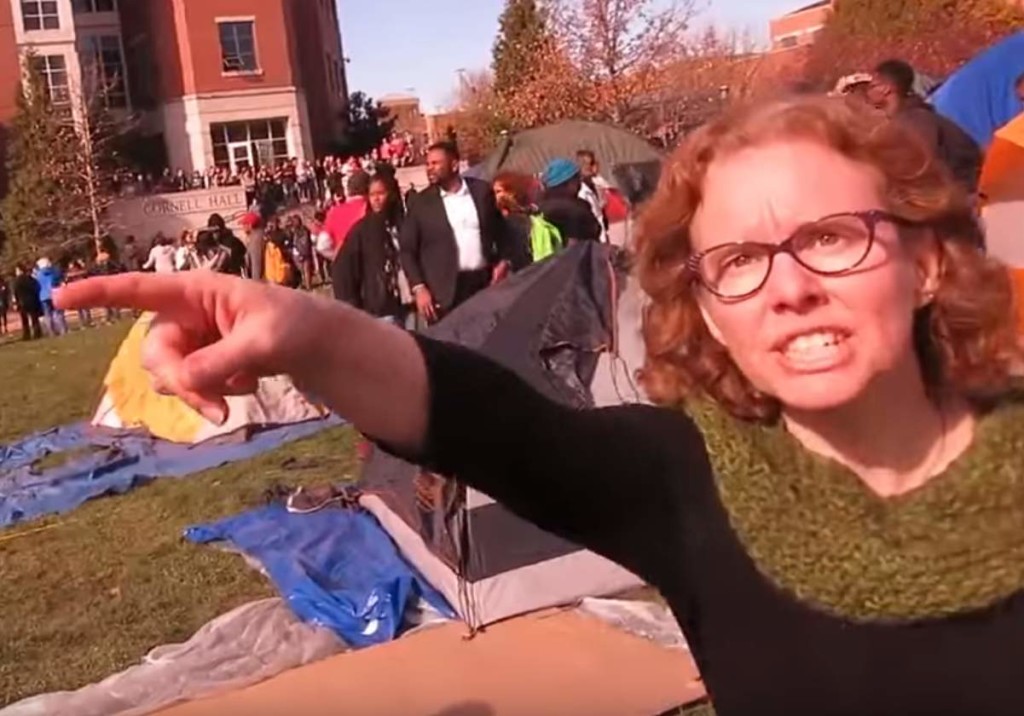
The recent spate of student protests that started at Yale and University of Missouri are self-evidently ominous. At Yale, students shouted down Yale professor Nicholas Christakis for failing to make them feel safe enough (“You should not sleep at night! You are disgusting!”). At the University of Missouri, student and faculty protesters and faculty allies forcibly barred student journalists from recording the public protest (which the journalists were legally entitled to do) and, when the journalists did not retreat fast enough, professor Melissa Click called out, “Who wants to help me get this reporter out of here? I need some more muscle over here.”
There have been apologies at Yale, resignations at Missouri, and copy-cat protests (and resignations) are starting to spread to other schools. At Claremont McKenna College in California, the dean of students replied to a Hispanic student’s public complaints with an attempted overture, writing in a student paper:
Would you be willing to talk with me sometime about these issues? They are important to me and the [Dean of Students] staff and we are working on how we can better serve students, especially those who don’t fit our CMC mold.
I would love to talk with you more.
Despite the dean’s obvious concern and goodwill, her use of the phrase “don’t fit our CMC mold” prompted two CMC students to threaten a hunger strike. The dean promptly resigned.
I have a lot of good friends who are supportive of the protesters at Missouri, Yale, and elsewhere. I know that they are good people. They are guided by principles of justice and equality that I also value. And so, for me, the thing I have wrestled with the most over the last week has been the attempt to reconcile the dissonance between their stated principles and motivations and the outcomes: hair-trigger intolerance, a climate of fear, and disregard for free speech.
I have come to this belief: when good intentions pave the path to Hell, it is because better principles have been allowed to fall by the wayside. The reason this can happen, the reason there is a tendency to let go of better principles, is that once they become ubiquitous we no longer recognize their importance. Unless we take the effort to remember the past, we will not understand how much we stand to lose.
Nowhere is this contrast more poignant than at Yale. Early in the controversy, the President Salovey wrote an email reiterating the school’s commitment to free speech, “not as a special exception for unpopular or controversial ideas but for them especially.” This stance is official Yale policy thanks to the Woodward Report. This document, formally called the Report of the Committee on Freedom of Expression at Yale, was issued in 1975 and the first section of it was adopted as official policy. It’s not every policy that begins with lofty prose and poetry, but the first section of the Woodward Report begins with this quote from John Milton:
And though all the winds of doctrine were let loose to play upon the earth, so Truth be in the field, we do injuriously by licensing and prohibiting to misdoubt her strength. Let her and Falsehood grapple; who ever knew Truth put to the worse, in a free and open encounter.
Next come these words from Oliver Wendell Holmes:
If there is any principle of the Constitution that more imperatively calls for attachment than any other it is the principle of free thought – not free thought for those who agree with us but freedom for the thought that we hate.
The section then culminates with a stirring defense of the principle of free speech:
The conclusions we draw, then, are these: even when some members of the university community fail to meet their social and ethical responsibilities, the paramount obligation of the university is to protect their right to free expression. This obligation can and should be en forced by appropriate formal sanctions. If the university’s overriding commitment to free expression is to be sustained, secondary social and ethical responsibilities must be left to the informal processes of suasion, example, and argument. [emphasis added]
The principle of free speech is more than narrow legal statutes. It is an attitude of protecting unpopular views from silence and overbearing retaliation. The arguments of student protesters and their defenders are an explicit repudiation of this broad vision for free speech. Therein lies the danger. The pursuit of justice, divested of the burden of protecting unpopular opinions and unflinching fidelity to truth, risks veering into vigilantism and fanaticism. No matter how noble the ambitions, when we no longer take it upon ourselves as a matter of principle to defend unpopular ideas and to allow truth to wrestle falsehood in a “free and open encounter,” we abandon the first right and cornerstone of our pluralistic society.
2.Liberal Intolerance
The protests at Missouri and Yale should not be analyzed in isolation. They are part of a disturbing trend that has attracted criticism not only from the right but increasingly from the center and left. It will be worth our time to survey some of that context before we move on.
Andrew Sullivan launched the mainstream movement to legalize gay marriage when he wrote “Here Comes the Groom” for the New Republic in 1989. Twenty-five years later, he looked on in horror as the movement he had helped to launch spiraled out of control in what Sullivan described as “McCarthyism applied by civil actors.”
Sullivan was reacting to the forced resignation of Mozilla CEO Brandon Eich. Only days after being promoted to lead the company he had helped found in 1998, word spread across the Internet that Eich had donated $1,000 to California’s anti-gay marriage Proposition 8 in 2008. Although Mozilla had long been committed to diversity and support for gay rights, although there was not a single alleged incident of prejudicial conduct or statements by Eich, and although Eich publicly committed to preserve Mozilla’s progressive culture and policies, this donation tainted him irrevocably. The Internet-based outrage spread across Twitter and soon other companies (like dating site OKCupid) got into the act of pressuring Mozilla to fire Eich, who stepped down on April 3, 2014 after being CEO for less than two weeks. The next day, Sullivan wrote his blog post, arguing that:
When people’s lives and careers are subject to litmus tests, and fired if they do not publicly renounce what may well be their sincere conviction, we have crossed a line…This is the definition of intolerance… It’s staggering to me that a minority long persecuted for holding unpopular views can now turn around and persecute others for the exact same reason. If we cannot live and work alongside people with whom we deeply disagree, we are finished as a liberal society.
At about the same time, John McWhorter wrote an article for Time: “‘Microaggression’ Is the New Racism on Campus.” He argued that “the nature of microaggressions — subtle, unintended, occurring in the hustle and bustle of social interaction — is such that they will never cease to exist entirely,” and that this ubiquity entailed that “being white is, in itself, a microaggression.” This, he wrote, “is just bullying disguised as progressive thought.”
In December 2014, Jeannie Suk wrote “The Trouble with Teaching Rape Law” for The New Yorker. Rape law was not taught in law school until the mid-1980s, she writes, because rape was not taken seriously. Feminists fought to change that, and when they won law schools began to teach rape law. Now, however, some law professors are starting to abandon the topic again, this time because of hypersensitive students who are afraid of being traumatized. Suk describes just how far their paranoia extends:
Student organizations representing women’s interests now routinely advise students that they should not feel pressured to attend or participate in class sessions that focus on the law of sexual violence, and which might therefore be traumatic. These organizations also ask criminal-law teachers to warn their classes that the rape-law unit might “trigger” traumatic memories. Individual students often ask teachers not to include the law of rape on exams for fear that the material would cause them to perform less well. One teacher I know was recently asked by a student not to use the word “violate” in class—as in “Does this conduct violate the law?”—because the word was triggering.
In January 2015 Jonathan Chait wrote “Not a Very PC Thing to Say” for New York Magazine. He documented numerous examples of harassment and intimidation of those who dared question conventional socially liberal dogma and concluded that “the new political correctness has bludgeoned even many of its own supporters into despondent silence.” In February, Jon Ronson wrote “How One Stupid Tweet Blew up Justine Sacco’s Life,” for the New York Times Magazine. He observed that
In the early days of Twitter, I was a keen shamer. When newspaper columnists made racist or homophobic statements, I joined the pile-on. Sometimes I led it…Still, in those early days, the collective fury felt righteous, powerful and effective. It felt as if hierarchies were being dismantled, as if justice were being democratized. As time passed, though, I watched these shame campaigns multiply, to the point that they targeted not just powerful institutions and public figures but really anyone perceived to have done something offensive. I also began to marvel at the disconnect between the severity of the crime and the gleeful savagery of the punishment. It almost felt as if shamings were now happening for their own sake, as if they were following a script.
In February, Laura Kipnis wrote “Sexual Paranoia Strikes Academe” for the Chronicle of Higher Education. She criticized new dating policies strictly barring dating between students and professors for infantilizing students and dismissed the “prohibition and sexual terror surrounding the unequal-power dilemmas of today.” She went on:
If this is feminism, it’s feminism hijacked by melodrama. The melodramatic imagination’s obsession with helpless victims and powerful predators is what’s shaping the conversation of the moment, to the detriment of those whose interests are supposedly being protected, namely students. The result? Students’ sense of vulnerability is skyrocketing.
As a result of her article, Kipnis was the subject of a formal Title IX inquiry.
In March, Asam Ahmad wrote “A Note on Call-Out Culture” for Briarpatch Magazine (the sort of publication that, according to its Wikipedia page, “is printed by union labour on FSC-certified paper using vegetable-based ink.”) He noted that “It isn’t an exaggeration to say that there is a mild totalitarian undercurrent not just in call-out culture but also in how progressive communities police and define the bounds of who’s in and who’s out.”
In April Damon Linker wrote in “The shunning of Ryan T. Anderson: When support for gay marriage gets ugly” that the outrage that erupted when a profile of Ryan T. Anderson was posted on his alma mater’s website and the school’s decision to remove the profile were
depressing signs that liberal public opinion is evolving in the direction of theological certainties and illiberal forms of intolerance. These so-called liberals want Anderson to be shunned. Expelled from the community. Excommunicated from civilized life. Ostracized from the ranks of the decent. That is something that should trouble all fair-minded Americans.
In June, an anonymous professor wrote an article for Vox: “I’m a liberal professor, and my liberal students terrify me.” He explains that the thought of possibly offending one of his liberal students caused him “to comb through my syllabi and cut out anything I could see upsetting a coddled undergrad, texts ranging from Upton Sinclair to Maureen Tkacik,” and he laid much of the blame at the feet of “a totalizing, simplistic, unworkable, and ultimately stifling conception of social justice.”
In September, Greg Lukianoff and Jonathan Haidt wrote “The Coddling of the American Mind” for The Atlantic. They described some of the student protests that had already occurred by then as “border[ing] on the surreal.”[ref]In the week between my first draft of this article and posting it, news came out that the University of Ottawa canceled a yoga class for cultural appropriation. Absurd stories like this are too numerous to document.[/ref] They went on to contrast the current movement to the wave of political correctness that swept academica in the 1980s and 1990s:
The current movement is largely about emotional well-being. More than the last, it presumes an extraordinary fragility of the collegiate psyche, and therefore elevates the goal of protecting students from psychological harm. The ultimate aim, it seems, is to turn campuses into “safe spaces” where young adults are shielded from words and ideas that make some uncomfortable. And more than the last, this movement seeks to punish anyone who interferes with that aim, even accidentally. You might call this impulse vindictive protectiveness. It is creating a culture in which everyone must think twice before speaking up, lest they face charges of insensitivity, aggression, or worse.
All of these writers come from the left or the center of the American political spectrum. And all of these writers are united in their belief that a sea-change is taking place within American society. Something is wrong. Some new trend is tying together extreme emotional sensitivity, simplistic notions of social justice, and intolerance of thought or speech. What is going on? And how did it get so bad?
The best explanation comes from an academic article: “Microaggression and Moral Cultures” by Bradley Campbell and Jason Manning.[ref]The article was brought to my attention by Jonathan Haidt’s Righteous Mind blog, where you can read a good summary of the article. I have read the entire article, but I haven’t found a publicly accessible link to the full text that I can share.[/ref]
In their article, Campbell and Manning describe social evolution from honor cultures to dignity cultures and on to the dawning of a new culture: the culture of victimhood. Honor cultures tend to arise where central authority is weak. This leads to “self help” justice, so named “because it involves the aggrieved taking matters into their own hands rather than relying on the legal system.” Honor cultures are typified by extreme sensitivity to insult combined with a tendency towards direct confrontation. When more powerful formal authorities arise, honor cultures give way to dignity cultures. In a dignity culture, “self help” justice is itself punishable by the authority. As a result, minor offenses are ignored and major offenses result in formal appeals to central authority. In contrast to honor cultures, dignity cultures have low sensitivity and an aversion to direct confrontation.
Victimhood culture is something new, and according to Campbell and Manning it has evolved on college campuses in response to four key factors:
- Increased equality and diversity. This may seem counter-intuitive, but Campbell and Manning point out that the more equal and diverse a society becomes, the less tolerant it is to violations of equality or diversity. Thus, the increase in equality and diversity on college campuses since the 1960s and 1970s creates an atmosphere where people are hypersensitive to comparatively minor violations of diversity or equal status.
- The legal and administrative authority that college officials wield over their students has increased dramatically in recent decades. This means that students are more and more inclined to appeal to administrators for redress of insults or offenses.
- Social atomization–the breakdown of small organizations like clubs, extended family networks, and mutual aid societies–makes it harder for individuals to respond to offenses directly. When these groups were stronger, they created a tendency toward direct confrontation because the group would support you. In their absence the tendency to avoid direct confrontation with an offender and seek official assistance has increased even more.
- Social networking technology allows individuals to propagate a message to a very large audience. This factor is perhaps the most decisive, because it is the potential to reach a vast audience that allows offended parties to use public pressure to coerce university authorities into assisting them.
Campbell and Manning make one additional key point: appealing for official assistance to redress a grievance is significantly more likely to succeed when the grievance is seen as part of a pattern of offenses that target an identifiable, victimized group. That is why there is such a close connection between social justice and victim culture: victimhood is at its most potent when it is seen as a symptom of systematic oppression.
The Campbell and Manning model is a theoretically sound and compelling explanation for the observations of Sullivan, McWhorter, Chait and the rest. The reason it feels as though there is a seismic shift going on, with college students becoming hypersensitive to perceived offenses to diversity or equality resulting in draconian punishment, is that such a seismic shift is indeed taking place.
3. Instrumental Victimhood
Campbell and Manning chose to study microagressions because “the anatomy of microaggression… has broader implications,” not because victimhood is relegated only to this particular tactic. On the contrary, they write that other “tactics such as hunger strikes, hate crime hoaxes, and protest suicides” are all potent weapons that can implement the strategic logic of victimhood culture.
The strategic logic of honor culture is to deter attacks by maintaining a reputation for violent reprisal. The strategic logic of dignity culture is to avoid unsanctioned feuds or conflicts by ignoring offenses unless/until they are so severe that the central authority will decisively take your side. The strategic logic of victimhood culture is to proactively construct a narrative of perpetual victimhood that will enlist the central authority on one’s behalf while simultaneously providing immunity from that central authority.
This gets to the fundamental problem with victimhood culture: the perverse incentives of acquiring power through victimhood tend to the hijacking of genuine social injustice by those who seek power. Or, as Campbell and Manning bluntly put it, “whenever victimhood (or honor, or anything else) confers status, all sorts of people will want to claim it.”
As you can imagine, if victimhood has become a valuable social commodity, then the people most likely to be able to obtain it are those least likely to need it. Campbell and Manning make the same observation, remarking that “these campaigns for support do not necessarily emanate from the lowest reaches of society… rather… microaggression complaints and protest demonstrations appear to flourish among the relatively educated and affluent populations of American colleges and universities.” This is also why you will see ample evidence of social justice causes for blacks, gays, or women but will hear comparatively little about social justice activism for the mentally ill, young children, the unborn, or the infirm. It is not that blacks, gays, and women do not face systematic discrimination. They do. But these groups also include individuals who wield enormous social, political, and economic clout. And it is these individuals who are most able to powerfully establish a victimhood narrative and draft institutional authority into coming to their aid. The other categories, however, truly have no social capital. There are no industry tycoons or media moguls among the population of those living in psychiatric institutions , in foster homes, in their mother’s womb, or confined to their beds. And so it is no coincidence that the student who began the hunger strike at the University of Missouri comes from a prominent and extremely wealthy family.[ref]His father is a railroad executive whose compensation in 2014 totaled almost ten million dollars. The struggle is realer for some than others, apparently.[/ref]
Of course it is possible and even desirable for the most powerful members of oppressed communities to agitate for justice for those who are unable to do so as effectively. The problem, however, is that upper-class members of these groups may be so detached from the concerns of lower-class or ordinary members that—even despite their best intentions—their efforts may be unhelpful or even counter-productive.
This is another common theme from several of the articles we have seen already. Jeannie Suk, for example, describes how refusing to teach rape law rolls back decades of feminist activism. This fits with the U. S. Department of Justice observation that risk of rape is higher for women living in households with low income and rural households, not exactly the populations best represented at Harvard Law. Laura Kipnis also sees the paranoid fear of power imbalances as a repudiation of sexism, but—again—highly educated grad students are already in an position of relative power and privilege and so have the least to fear from the collateral damage of this particular victimhood narrative. As for race, John McWhorter has written that the social justice obsession with white privilege is practically useless and “seems almost designed to turn black people’s minds from what political activism actually entails.”
The worst-case scenario, of course, is when members of one of these groups act out in direct opposition to the interests of others within that group. Let’s explore one particular case to see how this plays out in practice. Just as with Campbell and Manning’s decisions to focus on microaggressions (instead of the full range of tactics available to victim culture), we will see that the anatomy of this controversy too has broader implications.
4. The Women You Are Not Supposed To See
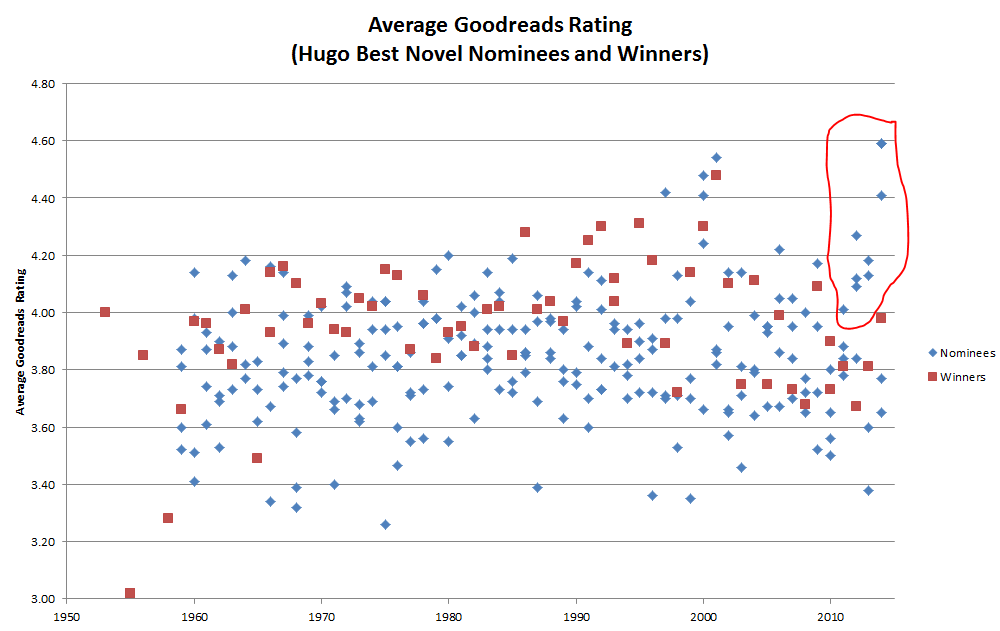
This year has been a tough one for the science fiction community. A bitter controversy erupted over the annual Hugo awards (think: Oscars for science fiction) and eventually attracted national and international media attention.[ref]My blog posts on this issue have been some of the most widely read on my blog, for example: Lots of Hugo Losers and Some Sad Puppy Data Analysis.[/ref]
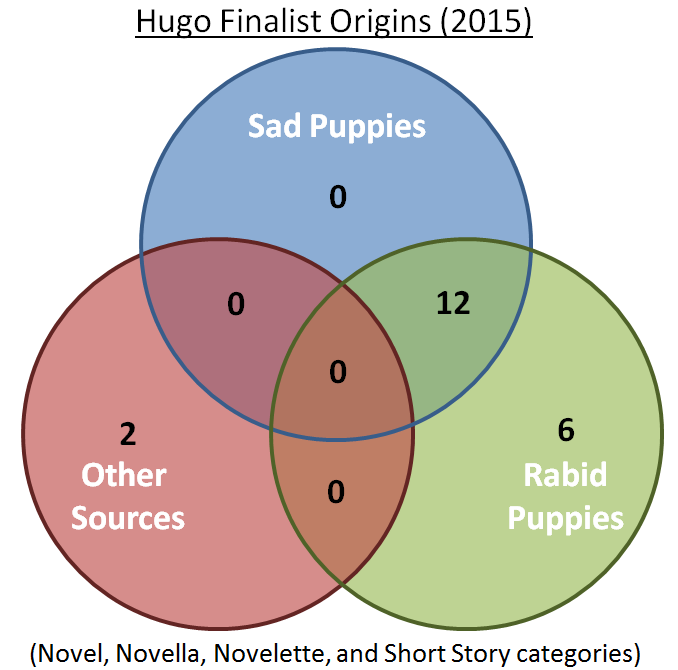
One side of the controversy consisted to two groups with unlikely names: the Sad Puppies and the Rabid Puppies. The Sad Puppies claimed that the Hugo awards were being dominated by an insular clique that privileged the right connections and the right politics over good writing. The Sad Puppies were led by Brad Torgersen this year, and under his leadership they sought to bring the awards back to the people. Their objective was to nominate a diverse slate of outsiders to break the social and political mold. The Rabid Puppies—spear-headed by Theodore Beale—took a different tack. If the Sad Puppies wanted to give the Hugos back to the people, the Rabid Puppies wanted to burn them down. The Rabid Puppies helped the Sad Puppy-nominated works make it onto the ballots just to provoke an angry reaction from science fiction’s many social justice-conscious writers and fans.
When the nominees were announced in April and it turned out that the Sad/Rabid Puppy nominations had swept much of the ballot, those angry reactions came fast and furious. The narrative that quickly emerged—promulgated by science fiction writers and fans with the assistance of sympathetic journalists in major outlets—was that the Puppies were a bunch of straight, white, males out to purge gays, minorities, and women from science fiction out of sheer homophobia, racism, and misogyny. This may seem like a cartoonish caricature of a wide swathe of the fanbase, but articles like Entertainment Weekly’s Hugo Award nominations fall victim to misogynistic, racist voting campaign show how seriously this narrative was taken.
The EW piece was so egregiously false that it was subsequently corrected, but the basic narrative was perpetuated in countless other venues. This is because victimhood culture requires control of narrative to a greater degree than honor culture or dignity culture. Honor culture relies on direct confrontation. Dignity culture downplays conflict until an appeal to formal authority is necessary and sure to win. Only victimhood culture treats the court of public opinion as a first resort.
To show how far journalists are willing to go in defense of their narrative, consider the most recent piece on the Sad Puppies from a major publication. That would be “Sci-Fi’s Hugo Awards and the Battle for Pop Culture’s Soul,” which Wired ran on October 30th, 2015. The piece, by Amy Wallace, did not indulge in subtlety. It was subtitled “Equality in a Digital Age.”
The most striking thing about the article are the choices Amy Wallace made in choosing whom to interview. She spoke to Brad Torgersen and Theodore Beale of the Sad and Rabid Puppies. She also spoke to several science fiction writers opposed to the Puppies. But there was one group in particular that Amy Wallace did not speak to. In fact, their names do not even appear in the article at all. They include people like Sarah Hoyt, Kate Paulk, Amanda Green, and Kary English. Who are they? Well, the first three are the leaders of this year’s Sad Puppies campaign and Kary English is one of the female authors nominated by last year’s Sad Puppies campaign. If you spend even a few minutes talking to them, which I did, you quickly see why Wallace wanted to steer clear. They threaten the narrative that vitcimhood culture depends on and that Wallace was so careful to help fabricate.
Let’s start with the fabrication. Leaving these women out of the picture is more than just an accidental omission. It is a deliberate decision to falsely characterize the leadership of the Puppies as all-male. “This time around, the leaders of the Puppies movement are sci-fi authors,” writes Wallace, before going on to name and discuss Larry Correia (who started the first Sad Puppy campaign), Brad Torgersen and Theodore Beale. But Sad Puppies 4 is active right now. It was officially announced on September 3. Their official website is not hard to find. What’s more, the leadership of Sad Puppies 4 had been common knowledge for months before September’s announcement. There is no way that Wallace did not know these women existed. So make no mistake, when Wallace talks about “the leaders of the Puppies movement,” she is leaving out the leaders that she doesn’t want to talk about.
Nor are these leaders late-comers. Sarah Hoyt was the first choice to head Sad Puppies 3 (ahead of Brad Torgersen). She had to drop out due to health concerns, and he took over at the last minute. This is something Wallace would have easily learned if she had talked to Hoyt, but she never did. According to Torgersen:
Amy Wallace lied to me. I knew she would be slanting her coverage against Sad Puppies, that wasn’t surprising. What surprised me was the fact that she promised me on the phone that she would contact Sarah A. Hoyt for the article Amy was doing for WIRED, and she never did.
I confirmed this with Sarah Hoyt myself. I also spoke with Kate Paulk, Amanda Green, and Kary English. Each and every one of them confirmed to me that Wallace made no attempt to contact any of them. [ref]Some of them even checked rarely-used email accounts for me, just to confirm that they hadn’t missed anything. They hadn’t.[/ref]
Of course, if you spend a few minutes talking to them, it’s not hard to see why Wallace wanted to stay clear. Her version does not survive contact with the reality they are more than happy to dish out. For example, Hoyt told me, when I asked her what she thought of Wallace’s article and it’s omissions, that “I’m tired of these people, who are the de facto power mongers and gatekeepers, speaking power to truth.” She continued, “These people want to be heroes for doing nothing. They are the ones silencing women.”
Upon learning that she, Hoyt, and Green had been scrubbed from Wallace’s account, Paulk told me “That’s so much bad faith you could open the gates to Hell with it.” Paulk went on to say, speaking of women who do not toe the right ideological line, that “We’re the women who are invisible. We’re ‘traitors to our gender.’”
And this brings us back to the main point of this example: what kind of feminism is it, exactly, that calls for the erasure of women?
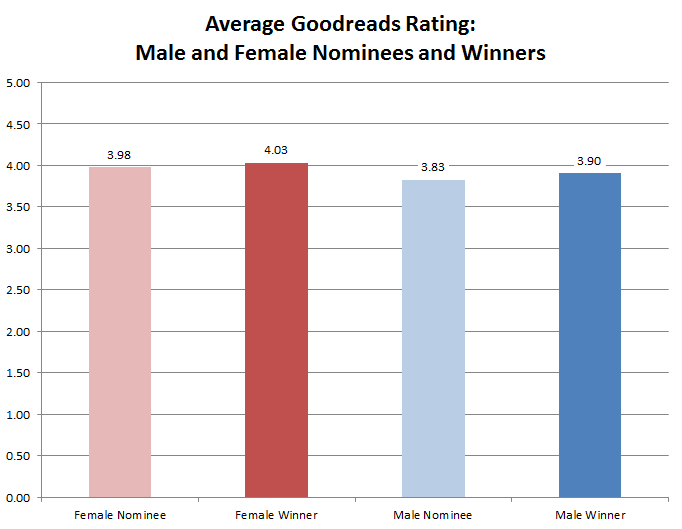
Kary English is a good person to ask about that. English refused to withdraw her short story “Totaled,” from contention when it ended up on the Sad Puppy and Rabid Puppy nomination lists. English’s participation with the Sad Puppies has nothing to do with political alliances. She is a liberal with no love for Theodore Beale and the Rabid Puppies. In fact, a large part of the reason she continued to support the Sad Puppies was because she believed they were doing a better job of presenting a diverse set of works. “Sad Puppies 3 was run by a brown guy and a man in an inter-racial marriage,” she told me, referring to Larry Correia (who started the first Sad Puppies campaign and is Hispanic) and Brad Torgersen (who is married to a black woman). She went on, “The list included women authors, queer authors, and non-neurotypical authors. It included conservatives, liberals and authors whose politics no one knows.” A reader of Amy Wallace’s article—and a great many more—would know nothing of that.[ref]Wallace did mention that Torgersen is married to a black woman and that Beale is Native American. She did not mention that Correia is Hispanic, nor did she give the indication that the Sad Puppy nominated works were ideologically and demographically diverse.[/ref]
Because she refused to back down, English was punished by being “no-awarded” at the Hugos. Even though her story beat out all contenders, voters preferred to give out no award at all rather than let a woman associated with the Puppies win any way. When “No Award” was announced in her category, the audience applauded vindictively. (Booing “No Award” was barred by the emcee, who was an open critic of the Sad and Rabid Puppies.)
Not that backing down would have helped matters. English compares the way she and other nominees were treated to witch dunkings:
Once you’ve been accused of being a fascist, you get thrown into a pond with your arms and legs bound. If you’re innocent, you’ll withdraw. You’re dead and drowned as far as the award goes, but at least you’re not a fascist, right? If you stay in, if you float, you’re guilty and you’ll be burned at the No Award stake. Evidence? Who cares about evidence. If you were innocent, you’d have withdrawn.
And as for poor treatment of women, English points out that this does not seem to be a problem coming from the Sad Puppies side:
The women who remained on the Sad Puppies list were systematically attacked. We were called fascists, racists and homophobes despite the fact that there was zero evidence against us. We, along with our work, were dismissed as tokens and shields. Multiple media reports claimed that the Sad Puppy authors were all male. This is sexism. This is erasure. Where were our defenders and allies?
5. The Future of Social Justice Activism
I chose this example for two reasons. First, it illustrates how far the social justice / victimhood culture phenomenon has spread beyond the borders of college campuses. Where do liberal humanities and social science students go when they graduate? Well, a good number of them become journalists and authors, and in this way the social mutation of victimhood culture escapes the borders of the campus petri dish where it originated.
Second, it underscores the extent to which social justice activists—when infected with the values and tactics of victimhood culture—repudiate their own principles. Amy Wallace’s story for Wired—a story that was entirely typical of media coverage—reveals the extent to which feminists defending feminism are willing to sacrifice the dignity, voices, and identities of any women who get in their way.
This isn’t a critique of the principles of social justice. This isn’t an attack on equality, diversity, or the existence of systematic oppression. But it is an indictment of what happens when inattentiveness to other considerations—considerations of pluralism and truth and free inquiry—allows fervor to drift toward fanaticism. And it is a warning that, within the context of victimhood culture, social justice activism is particularly prone to being hijacked by upper-class activists who—intentionally or not—increasingly deploy the rhetoric and tactics of social justice activism not for the sake of justice, but for the sake of power.