53% of white women voted for Trump.
In the circles I run in, there was tons of coverage and discussion about the myriad comments Trump has made over the years that many of us consider blatantly sexist. When the Hollywood Access tape came out, I took (and still take) his comments as an admission of sexual predation, a topic that means a great deal to me. I was already a #NeverTrump conservative, but the Hollywood Access tapes made it much more difficult for me to understand how people of good conscience, especially women, could vote for this man.
My feed started to include articles such as The Atlantic’s “The Revolt of the Conservative Woman” and viral tweets from conservative women feeling betrayed by their party’s defense of Trump. Between his apparent gross disrespect of women and the opportunity to elect the first female president, I thought women would vote in droves for Clinton and against Trump. Article’s like FiveThirtyEight’s “Women are Defeating Donald Trump” seemed to think so too.
But clearly I was missing some major parts of the puzzle. (Apparently a lot of us were, including the pollsters.) As Walker pointed out recently, Trump’s support among (all, not just white) women was only slightly lower than the average for Republican presidential candidates since 2000 (42% compared to an average of 44.2%). Clinton’s support among women was exactly average for the Democratic presidential candidates since 2000 (54%). Women weren’t driven to the polls to vote against Trump or for Clinton—overall turnout among women was only 1% higher than in 2012.
So what happened? What pieces of the puzzle was I missing, that women were neither particularly repelled by Trump nor particularly inspired by Clinton?
Maybe it was bigotry.
Predictably, some of my leftist friends think the missing puzzle pieces are racism and (internalized) sexism. I’ve seen repostings of LV Anderson’s piece at Slate (“White Women Sold Out the Sisterhood and the World by Voting for Trump”), which is filled with explanations like this:
What leads a woman to vote for a man who has made it very clear that he believes she is subhuman? Self-loathing. Hypocrisy. And, of course, a racist view of the world that privileges white supremacy over every other issue.
Sarah Ruiz-Grossman at Huffington Post authored a letter to white women that started with “Fellow white women, I’m done with you.” In sync with a lot of the commentary I’ve read, it showed no curiosity as to the perspectives, hopes, fears, or values of millions of women that led them to vote for Trump (or at least not vote for Clinton). Instead, and again, it simply told them what they didn’t care about, what their moral failings were, and what they must do now.
While I appreciate the frustration, I think this approach is an awful strategy. Lambasting people, especially conservatives, for bigotry has not been terribly effective at changing their minds (or votes). Berating the other side seems to mostly get them to tune out entirely when the inevitable accusations of prejudice begin. And the rampant shaming of Trump supporters clearly did nothing to dissuade them throughout the primaries (when shaming was coming from conservatives and liberals alike) or the rest of the election. Why would it work now, when they’ve won? They have less reason than ever to be concerned about the opinions of people who show no understanding of their perspectives or interest in their wellbeing.[ref]I think it would be great if both sides would show more genuine curiosity in where the other is coming from, both for the sake of treating each other kindly and for the sake of a functional pluralistic society. But that’s already an uphill battle, and it’s made all the less likely by assigning people the worst motivations and then yelling at them.[/ref]
But it’s not just that I think accusing people of bigotry is poor strategy; I think it’s poor reasoning too. In this post I go through three theories of how voting for Trump was bigoted and explain whether I think those theories make sense.
Theory 1 – Internalized sexists: women voted for Trump instead of Clinton because they are sexist against female candidates.
How Trump measured against Clinton is a major factor. The pantsuit nation adored Clinton, of course, so for them this was no contest at all. But we aren’t looking into what HRC’s biggest fans thought; we’re exploring the millions of women who disagreed.[ref]Including, in all likelihood, the left-leaning women who had preferred Sanders to Clinton by wide margins. I expect the perception that the DNC unfairly backed Clinton over Sanders did not help Clinton get the vote out in the end.[/ref]
It’s not that everyone who voted for Trump thought he was wonderful: exit polls show that 20% of people who voted for Trump had an overall unfavorable opinion of him. Nearly a quarter of Trump voters said he wasn’t qualified for or did not have the temperament to be president, and a full 17% of people who voted for Trump to be President said they would be “concerned” if he were elected!
But 28% of Trump voters said they chose him mainly because they disliked Clinton. Trump received about 60M votes, which would mean about 17M cast their votes primarily as a vote against Clinton. Along the same lines, while voter turnout for Trump was slightly lower than it had been for Romney, voter turnout for Clinton was much lower than it had been for Obama.
Some will argue that these numbers show sexism: people so rejected the idea of a female leader they either stayed home or voted for someone they despised just to stop Clinton. Actually women get accused of sexism no matter which way they vote: Women who backed Clinton are accused of bias, just “voting with their vaginas,” and the rest of us are accused of not voting for her because we’re misogynists. It’s a lose-lose.
But these theories ignore the fact that women don’t generally vote based on gender, and gender stereotypes end up being less relevant than party affiliation in voting decisions. In other words, we vote based on political positions. The reality is that most of the women voting for or against Clinton did so based on a variety of competing concerns and priorities, just as most men choose their candidates.
CNN reported that millennial women in particular “rejected the notion that gender should be a factor in their vote.” As FiveThirtyEight put it:
Clinton’s stunning loss Tuesday night showed that issues of culture and class mattered more to many American women than their gender. The sisterhood, as real sisterhood tends to be, turned out to be riddled with complications.
On average, for the last 5 presidential elections[ref]When I originally linked to the New York Times, it had a section for viewing election results going back decades. If you can’t see this section, word search “2008” and it should come up.[/ref], 89% of Democrats chose the Democratic nominee and 91.4% of Republicans chose the Republican. Last week 89% of Democrats chose Clinton and 90% of Republicans chose Trump. If internalized sexism were a major factor in terms of female nominees, we’d expect 2016 to show a drop in Democrats voting for the Democrat (as internally sexist Democratic women abandoned Clinton) and perhaps even a jump in Republicans voting for the Republican (as internally sexist Republican women were motivated to stop Clinton). But there was no such change.
Similarly, if internalized sexism was a major factor we’d expect Clinton to get a lower proportion of women’s votes compared to previous Democratic nominees. Yet, as mentioned above, she got exactly the average proportion of women Democratic nominees have had in the last five presidential races. Or, if we’re operating under the idea that only conservatives can be bigots, we’d at least expect a higher proportion of women to vote for Trump in order to stop Clinton. Yet Trump got just slightly less than the average proportion of women Republican nominees have had for the last five races.
If anything, these stats suggest women weren’t influenced by gender at all.
Theory 2 – Indifference to sexism: women cared more about party lines than taking a stand against Trump’s misogyny.
There are several assumptions embedded in this line of thinking: (A) The women who voted for Trump accessed the same information we did about him. (B) When they assessed that information, they came to the same conclusions we did about the degree of Trump’s misogyny. (C) There was nothing else in the balance for them in this election that could have meant more to them than Trump’s misogyny.
2a. Trump voters were likely accessing different information.
Hopefully it’s not a secret that conservatives and liberals consume different media. I wish I had time to do an entire blog post on how drastically this impacts our views of each other and of our political landscape. But the main point is we should be very careful when assuming that everyone else—especially people that run in different social circles and already hold different perspectives—“knows” the same “truths” we know. Which stories get reported and how they’re described varies a lot, and sadly, at least in my experience, most people don’t look for sources from worldviews they don’t hold. Or, if they do, it’s not in an attempt to observe and understand, but to feel outraged and argue.
So when John Oliver does a witty, biting piece on “making Donald Drumpf again” and you see it reposted over and over, that doesn’t mean everyone saw it. The people who already hated Trump were a lot more likely to see it than anyone else. Late night comedy is, after all, a bastion of liberal derision.

2b. Trump voters were likely interpreting information in different ways.
That’s not to suggest Trump supporters were wholly unaware of criticisms against him. I think it’s unlikely, for example, that many Trump supporters didn’t at least hear about the Hollywood Access recording. But the context in which conservatives in general, and enthusiastic Trump supporters specifically, interpreted that was often quite different than how leftists saw it.
Many people (including me) were disgusted and horrified by Trump laughingly talking about getting away with kissing and groping women without their consent. But many others mostly heard politically-motivated faux outrage. The same people so focused on Trump’s comments and the sexual assault allegations against him remained dismissive or defensive about the long history of sexual misconduct and assault allegations against Bill Clinton—and Hillary Clinton’s role in silencing Bill’s accusers. Clinton fans retorted that Hillary isn’t responsible for Bill’s behavior, but that misses the point. She’s responsible for her behavior: she referred to these women as “floozy,” “bimbo,” and “stalker,” and put great effort into “destroying” their stories.

Good luck telling conservatives they must take a principled stand against sexual assault while refusing to acknowledge that the Clintons basically embodied rape culture.
Of course the Hollywood Access tapes are only one example of Trump’s sexism, but the pattern remains the same. Whatever example you point to, if outraged accusations of bigotry are coming from leftists or the media, conservatives are extremely skeptical. In fact, getting back to point 2a, conservative circles are more likely to have articles about people who made up stories of hate crimes – stories which, before being shown to be false, often caused viral online outrage (as well as extensive donations to the alleged victim).[ref]This is also why many conservatives aren’t reacting the same way to the stories of hate crimes in the wake of the election. They’re not thinking “I’m fine with that happening.” They’re mostly thinking “I don’t believe that is actually happening.” I’ve seen several conservative friends repost this explanation instead.[/ref]
I find this problem very frustrating. I do believe the left is too quick to claim bigotry, but I believe the right is therefore too quick to dismiss actual bigotry. Robby Soave of Reason.com summarized this view well:
[It’s] the boy-who-cried-wolf situation. I was happy to see a few liberals, like Bill Maher, owning up to it. Maher admitted during a recent show that he was wrong to treat George Bush, Mitt Romney, and John McCain like they were apocalyptic threats to the nation: it robbed him of the ability to treat Trump more seriously. The left said McCain was a racist supported by racists, it said Romney was a racist supported by racists, but when an actually racist Republican came along—and racists cheered him—it had lost its ability to credibly make that accusation.
Kirsten Powers explained the same idea in terms of misogyny:
After all, these same voters have watched as every Republican candidate in recent memory has been accused of waging a “War on Women.” If Democrats are going to claim that Mitt Romney and John McCain hate women (and they did), then they shouldn’t be surprised when voters ignore them when they say Donald Trump hates women. If every Republican is a misogynist, then no Republican is.
I don’t believe the right’s resistance to recognizing bigotry is all the left’s fault. I think that’s a factor, but ultimately we’re all responsible for assessing each situation and trying to be fair-minded about it.
Even so, I think many conservatives viewed the outrage over Trump as nothing more than yet another chapter in a long history of selective and manufactured leftist outrage[ref]Scott Alexander (who describes Trump as “super terrible”) does a great job explaining the ways many of the most common examples of Trump’s bigotry could be viewed as misconstrued or overblown.[/ref], and so they discounted it. So even if they had watched John Oliver, they probably would have just rolled their eyes at another leftist show mocking conservatives again.
2c. Trump voters were weighing a lot of additional concerns apart from bigotry.
But there were a lot of conservatives who heard about the problems with Trump and were seriously concerned. Many of them became the #NeverTrump crowd, but others still voted for Trump. Why? Because they weren’t balancing the problems of racism and sexism against nothing. They were taking those issues and factoring them in with a lot of other issues, weighing each one, and coming to a decision. Even women who voted against Trump had other concerns they considered more important than sexism.
Many reject as ridiculous this concept of weighing multiple factors, saying it’s a weak excuse to try to cover up bigotry. They assert nothing could outweigh the civil rights threats Trump represents, and therefore the people who came down on Trump’s side, by definition, just didn’t care enough about civil rights.

Interestingly, I saw the same reductive thinking from conservatives trying to berate #NeverTrump people into voting for him. If you didn’t vote for Trump—if you voted for Clinton, or even if you voted third party—you must not care about massive government abuse and corruption, our country’s impending economic collapse under an overregulated welfare state, and, possibly above all, the killing of tens of thousands of babies.
Does that last part sound hyperbolic to you? Because, for a huge portion of the pro-life movement, that was the assertion. Many pro-lifers view abortion as morally equivalent to any other unlawful human death. If you want to imagine the abortion debate from a pro-life perspective, just replace the concept of “fetus” with “toddler,” and listen to how the arguments sound. So when Hillary Clinton campaigned on a platform of no restrictions through all three trimesters and requiring Medicaid to cover abortions, that was an absolute deal breaker for many people.[ref]Even most self-described pro-choicers think abortion should be illegal later in pregnancy. Meanwhile only 36% of voters believe Medicaid should cover abortions.[/ref] Abortion happens in this country roughly 1 million times a year. Imagine for a moment you were choosing between (1) a candidate who stirs racial animosity and blatantly disrespects women and (2) a candidate who unapologetically embraces policies making it legal to murder a million toddlers a year. Who would you pick?
If your first response is to explain why that second description is false, you’re missing the point. Yes, I understand that for many, abortion is nothing at all like killing a toddler and even the comparison is offensive. I’m not trying to convince anyone here how to feel about abortion. I’m trying to convince people that you can’t sincerely talk about what motivates others if you refuse to acknowledge their actual perspectives. People who voted for Trump could (a) recognize Trump’s racism and sexism, (b) care greatly about those issues, and (c) still believe the threats Clinton represented were more dire. The only way you can genuinely believe that every single vote for Trump represented at minimum a callous disregard for civil rights is if you ignore or dismiss the circumstances and value systems of millions of people.
Passion about abortion likely affected many of women who voted for Trump.[ref]As well as the 29% of Latinos who voted for him.[/ref] LV Anderson was aghast that more than half of white women would vote for a man who said he’d appoint Supreme Court justices to overturn Roe v. Wade. It is amazing to me that so many people are still taken off guard when women are antiabortion. Half of American women are against abortion, and that has been true since long before Trump entered the primaries. Yet each time thousands or millions of women don’t go for the pro-choice position, pro-choice people are just so surprised. This is another example of the same pattern: be totally unaware of what people have repeatedly said they care about, and then be surprised and angry when they vote for the things they said they cared about all along.
I’ve used abortion as an example of competing values, but it’s only one of many. A recent New York Times article profiled women who voted for Trump. While 22-year-old Nicole Been mentioned her deep opposition to abortion as part of her stance, other women discussed Trump’s approach to veterans, their own dire financial situations, and their disillusionment with Democratic efforts to improve their lives. Another New York Times article profiled college-educated women who voted for Trump; they, too, opposed abortion, but focused more on economic security and job and college prospects for their children.
Article after article about the parts of the nation that went wholeheartedly for Trump (including many counties that had previously voted for Obama twice[ref]FiveThirtyEight gives examples of where this applied to women: “In Iowa, a state Obama also won in 2008 and 2012, the class-tinged tale was much the same. White women without a college degree account for just over a quarter of voters in the state, and while Obama won them by 17 percentage points in 2012, Clinton and Trump split their support. Trump won the state by 10 percentage points.”[/ref]) describe recurring themes of economic and cultural despair, resentment at being derided by the rest of us, and the way economic and racial anxiety intertwine. (Here’s one or two more.)
Note that racial anxiety is one of the recurring themes. The left seems to want to reduce this narrative to bigotry and nothing more, and I’ve spent a lot of time here explaining why I think that’s inaccurate. But the right seems to want to reflexively deny bigotry had any part to play, and I don’t think that’s true either. At minimum there was certainly a racial component to Trump’s candidacy. Looming large in the support of Trump were concerns about minority groups getting unfair preferential treatment and resources, immigrants taking resources and increasing criminal activity, and terrorists threatening our safety.[ref]Many conservatives were not happy when the left seemed more interested in using the Pulse nightclub shooting to talk about gun control and the “hateful” culture of conservative Christians while ignoring that the shooting was conducted by a Muslim American who pledged his loyalty to ISIS.[/ref]
Theory 3 – Institutionalized sexism and racism – regardless of personal motivation, women who voted for Trump supported a platform that would disproportionately harm minority groups.
A major hurdle with discussions of racism and sexism is the use of the same words to mean very different things. In my right-leaning circles, “racism” generally means an individual’s disdain or animosity towards others based on race. Same thing with “sexism,” but based on sex. In my left-leaning circles, “racism” and “sexism” often mean individual disdain or animosity, but can also mean cultural norms and systemic and institutionalized systems that disproportionately negatively impact minority groups.
So when someone claims that a vote for Trump was racist, they could either mean (a) the person casting the vote has disdain or animosity toward people of other races or (b) the person casting the vote, regardless of his or her motivations, helped to uphold systems that have major negative impacts on women and nonwhite people.
The interesting thing about the “effects not intentions” version of racism is that it can be empirically verified. Motivations can be pretty complicated, multifaceted, and irrational. Effects can be objectively measured. So if “racism” (or sexism or Islamophobia or homophobia) is defined as “policies and practices that hurt these groups,” and if electing Trump ends up hurting these groups, then it follows that electing Trump was racism, by this definition.
3a. It’s reasonable to believe electing Trump will end up hurting these groups.
Trump campaigned on ending sanctuary cities, suspending visas, and deportation. If implemented, those policies would disproportionately affect undocumented immigrants (about half of which are Hispanic or Latino, followed by Asian) as well as American citizens from families with mixed citizenship statuses. Whether you agree with these policies or not, and whether you personally care how these policies affect others or not, it’s hard to deny that they will negatively impact immigrants and their family members who are American citizens.
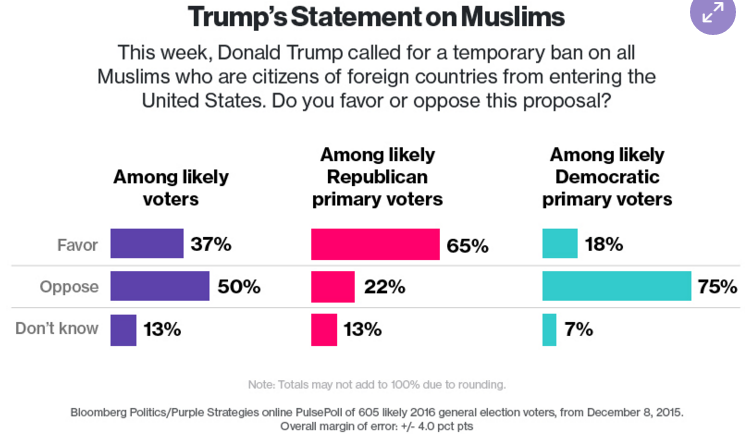
Trump has talked about requiring immigrants from predominantly Muslim countries to register upon entering the U.S. Alternatively he called for a ban on Muslims immigrating to the country; while he clarified this would not apply to American citizens, it’s hard to believe such policies and related rhetoric about Muslims won’t affect public perception of and reaction to Muslims already living here. The FBI has released data showing a 67% increase in hate crimes against Muslims in 2015. Some are worried this trend is related to Trump’s rise and campaign rhetoric; others say there are other factors–such as 2015 terrorist attacks–that likely played a part. But I think either of those reasons underscores the central point: when the public increasingly perceives a group as dangerous, violence against innocent people in that group becomes more likely.
It seems like Trump’s potential effects on African American communities have been less of a focus, but there are reasons for concern. (This link includes some reasons I think conservatives will dismiss as more faux outrage, but, for what it’s worth, I believe some of these points are pretty valid.)
While Trump didn’t propose specific policies against LGBT folk, the 2016 Republican Party platform did object to legalized gay marriage and take other positions seen as anti-gay. Because Trump was the Republican nominee and can now nominate SCOTUS judges, many believe he will work to adopt those Republican positions. I think it’s unlikely gay marriage will get overturned, but I don’t think it’s a certainty, and I see why many people are worried their marital status could be threatened.
Trump has a history that suggests a pretty disrespectful view of women, not to mention (again) his statements in the Access Hollywood recordings. To the extent women believe support for Trump signals societal dismissal of sexual assault, that belief could have another chilling effect on women reporting assaults and seeking help. I watched this play out on both the national level and with women I know personally after the Access Hollywood firestorm. Women (and men, for that matter) who have experienced sexual assault listened as friends and family who were Trump supporters minimized, dismissed, and, in my opinion, very generously interpreted Trump’s statements. That was difficult. Victims of sexual assault hear those reactions and believe the reactions would be the same if they came forward with their own stories. I can understand why people fear this kind of dismissal of sexual misconduct will only get worse now that Trump will be president.
A vote for Trump lent support to these policy proposals and attitudes, even if the person voting didn’t personally support one or any of the above. In this sense I think Theory 3 is truer than the other theories—I think a Trump administration will very likely make life harder for these groups.
3b. First problem: negative effects count as racism regardless of what they’re being weighed against.
Consider Trump’s campaign regarding Islamic terrorism. I do believe requiring (mostly) Muslim immigrants to register upon entering the country, or refusing to let them enter at all, will negatively affect the public’s views and behavior toward Muslim Americans and Muslim immigrants already here.
But I also recognize that the people who support these measures believe they will significantly increase our national security and safety. Based on my understanding of Theory 3, what Trump voters believe about these measures (and how those beliefs speak to their motivations) is irrelevant, because Theory 3 is all about effects on minority groups, not the intentions of the people pushing these policies. Whether they sincerely believe these measures will save American lives doesn’t change whether or not this approach is defined as racist.
And we’ve only talked about what they believe, not what is objectively true. Apparently NSEERS, the similar Bush-era program that required immigrant registration, was ineffective at preventing terrorism; it sounds like it was just more security theater, but in this case directed at specific groups. But suppose, hypothetically, immigrant registration made a huge difference in national security. Suppose—as I suspect is the belief of some who support this idea—that without immigrant registration we’d have more San Bernadino and Pulse nightclub shootings. Or another World Trade Center.
If these policies actually prevented terrorism deaths in our own country, does that change whether they are racist? If I understand Theory 3 correctly, it does not. In this way Theory 3 rings a bit hollow for me, because while it is at least technically accurate and objectively measurable (does X policy negatively impact Y community or not?), if it ignores all other factors I still consider it misleading.
3c. Second problem: conflating Theory 3 with Theories 1 & 2.
In my experience, the left frequently blurs the line between “negative impacts” and “personal animosity.” A great example is the Slate article “There’s No Such Thing as a Good Trump Supporter.” Chief political correspondent Jamelle Bouie[ref]Bouie also recently authored a piece on how Bernie Sanders, Elizabeth Warren, and other Democrats are wrong to talk about the populism that pushed Trump to victory without focusing on how racism was an integral part of Trump’s campaign. It will be interesting to see whether the Democratic party ultimately views this election as a call for them to do better at reaching the people who voted for Trump, or a call for them to take a stronger stance against anyone who upheld racism.[/ref] argues that Trump supporters do not merit empathy because they “voted for a racist who promised racist outcomes.” He cites other authors who have claimed Trump’s victory does not reveal an “inherent malice” in the populace (referring to the “personal animosity” definition of racism). Bouie counters with the “negative impacts” definition:
Whether Trump’s election reveals an “inherent malice” in his voters is irrelevant. What is relevant are the practical outcomes of a Trump presidency…If you voted for Trump, you voted for this, regardless of what you believe about the groups in question.
But, as the title of the piece suggests, Bouie is not condemning only the effects of voting for Trump; he’s condemning the Trump voters themselves. He asserts that it is myopic and even “morally grotesque” to suggest Trump supporters are good people. He compares Trump voters to the men in the early 20th century who organized lynchings (they “weren’t ghouls or monsters. They were ordinary.”) and the people who gawked and smiled at those lynchings (“the very model of decent, law-abiding Americana.”) He sums up: “Hate and racism have always been the province of ‘good people.’”
Note the switch here. Bouie is no longer talking about practical outcomes; he’s talking about hate. He has switched from the “negative impacts” definition of racism back to the “personal animosity” definition. So is he saying that most Trump supporters did not have inherent malice but should be condemned for the policies they supported? Or is he saying that anyone who can support Trump has to be, at least in part, motivated by hate?
And this is often how I see the conversation going. To (heavily) paraphrase:
Person A: If you voted for Trump, you’re racist.
Person B: I’m really not. I disagreed with a lot of what he said but I thought Clinton would do more damage in XYZ ways.
Person A: Yeah, you may not personally feel racist but you supported racist policies. It just shows you think the concerns of white people are more important than the actual human rights of everyone else.
Person B: That’s not what I think at all!
Person A: It’s not about what you personally think! It’s about what you supported!
And repeat.
In other words, in principle motivation is supposed to be irrelevant because racism is about effects, but in practice accusations of racism nearly always boil down to motivation—at best a selfish indifference and at worst outright malice. So, in principle, I think Theory 3 has some merit and is worth talking about. In practice, I find I just end up repeating the arguments I made for Theories 1 & 2.



 It turns out that favorite buzzwords and phrases like “racist,” “white privilege,” and “implicit bias” are often seen by these voters “as coded slurs. These terms don’t signal to them that they’re doing something wrong, but that their supposedly racist attitudes (which they would deny having at all) are a justification for lawmakers and other elites to ignore their problems…What’s more, accusations of racism can cause white Americans to become incredibly defensive — to the point that they might reinforce white supremacy. Robin DiAngelo, who studies race at Westfield State University, described this phenomenon as “white fragility” in
It turns out that favorite buzzwords and phrases like “racist,” “white privilege,” and “implicit bias” are often seen by these voters “as coded slurs. These terms don’t signal to them that they’re doing something wrong, but that their supposedly racist attitudes (which they would deny having at all) are a justification for lawmakers and other elites to ignore their problems…What’s more, accusations of racism can cause white Americans to become incredibly defensive — to the point that they might reinforce white supremacy. Robin DiAngelo, who studies race at Westfield State University, described this phenomenon as “white fragility” in